7. From a graph G P(G) = (Vp, Ep), is formed as follows: (V, E), with vertices v; E V and edges e; E E, the prism of the graph, Let V' be a copy of V with vertices v, and E' a copy of E with edges e'. Now V, = VUV', and E, = EU E'U {(vi, v²)\v; E V}. An example of a graph and its prism is shown below. (a) If a graph G has n vertices and k edges, find formulae for the number of vertices and the number of edges in P(G) in terms of n and k. (b) Explain why none of the following can be the prism of any connected graph: i. A graph with 9 vertices. ii. A graph with 10 vertices and 10 edges. iii. A simple graph with 3 edges.
7. From a graph G P(G) = (Vp, Ep), is formed as follows: (V, E), with vertices v; E V and edges e; E E, the prism of the graph, Let V' be a copy of V with vertices v, and E' a copy of E with edges e'. Now V, = VUV', and E, = EU E'U {(vi, v²)\v; E V}. An example of a graph and its prism is shown below. (a) If a graph G has n vertices and k edges, find formulae for the number of vertices and the number of edges in P(G) in terms of n and k. (b) Explain why none of the following can be the prism of any connected graph: i. A graph with 9 vertices. ii. A graph with 10 vertices and 10 edges. iii. A simple graph with 3 edges.
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
Please solve!
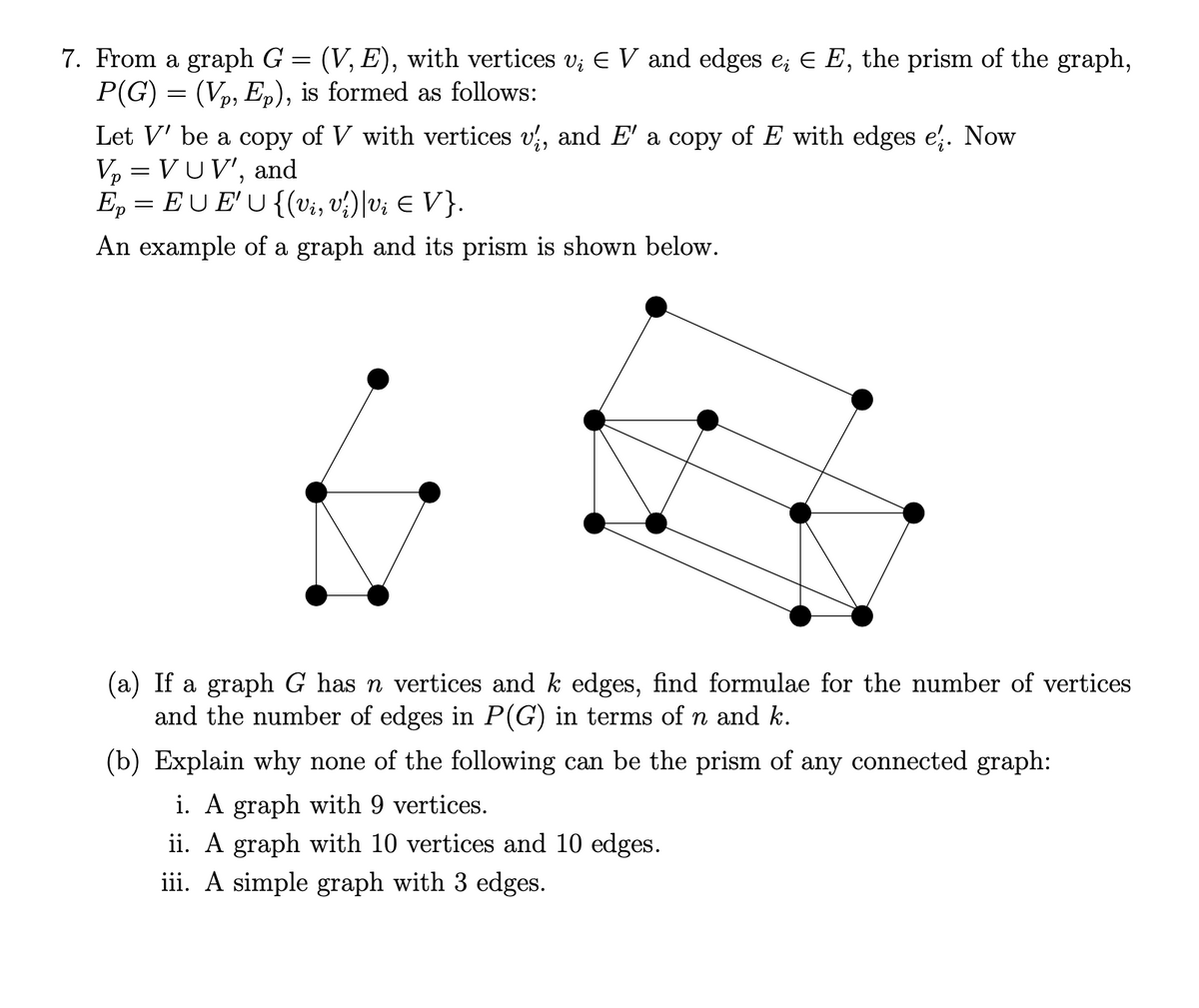
Transcribed Image Text:7. From a graph G = (V, E), with vertices v; E V and edges e; E E, the prism of the graph,
P(G) = (Vp, Ep), is formed as follows:
Let V' be a copy of V with vertices v, and E' a copy of E with edges e. Now
Vp = VUV', and
E, = EU E'U {(vi, v?)|v¿ E V}.
An example of a graph and its prism is shown below.
(a) If a graph G has n vertices and k edges, find formulae for the number of vertices
and the number of edges in P(G) in terms of n and k.
(b) Explain why none of the following can be the prism of any connected graph:
i. A graph with 9 vertices.
ii. A graph with 10 vertices and 10 edges.
iii. A simple graph with 3 edges.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

