8. Free-radical Cl• atoms can react with ozone in the region of the stratosphere known as the Ozone Layer, which protects life on Earth from the damaging UV-B and UV-C radiation bands. Use information this proposed mechanism for that process to answer the questions that follow: CI(g) + 03(g) → CIO(g) + O,(g) (b) Lewis Struct. of ClO: CIO(g) + O3(g) → Cl(g) +2 O,(g) :C1: 0: Cllg)+203(9)+CI019) CIDS)+30z19)+CIlg) Overall: 203(9)30219) (a) Write the overall reaction being proposed in the space provided above. AH =-285 kJ/molan (b)Draw a valid Lewis structure for the CIO molecule in the box, considering electronegativity while placing the unpaired electron. (c) Identify any intermediates and/or catalysts: ntermediate: CIO Caralyst:CI (d) Write the rate law assuming the first step is the rate determining step (the REAL MECHANISM): (e) Write the rate law assuming, incorrectly, that the second step is the rate determining step: (f) Circle the diagram below that best represents the REAL mechanism, and briefly exnlain uhu
8. Free-radical Cl• atoms can react with ozone in the region of the stratosphere known as the Ozone Layer, which protects life on Earth from the damaging UV-B and UV-C radiation bands. Use information this proposed mechanism for that process to answer the questions that follow: CI(g) + 03(g) → CIO(g) + O,(g) (b) Lewis Struct. of ClO: CIO(g) + O3(g) → Cl(g) +2 O,(g) :C1: 0: Cllg)+203(9)+CI019) CIDS)+30z19)+CIlg) Overall: 203(9)30219) (a) Write the overall reaction being proposed in the space provided above. AH =-285 kJ/molan (b)Draw a valid Lewis structure for the CIO molecule in the box, considering electronegativity while placing the unpaired electron. (c) Identify any intermediates and/or catalysts: ntermediate: CIO Caralyst:CI (d) Write the rate law assuming the first step is the rate determining step (the REAL MECHANISM): (e) Write the rate law assuming, incorrectly, that the second step is the rate determining step: (f) Circle the diagram below that best represents the REAL mechanism, and briefly exnlain uhu
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Chapter7: Covalent Bonding
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 81QAP: It is possible to write a simple Lewis structure for the SO42- ion, involving only single bonds,...
Related questions
Question
Can you help me?
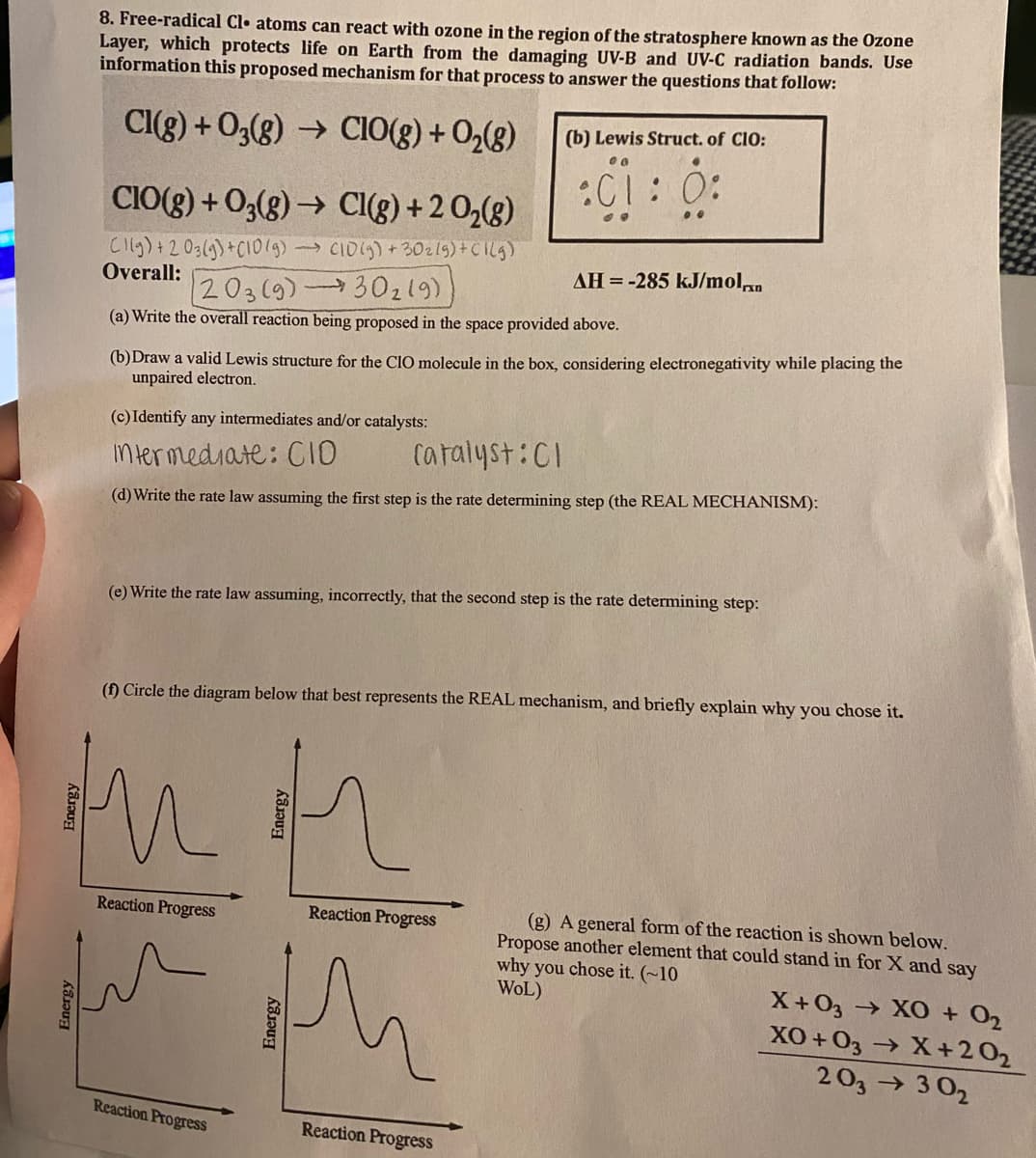
Transcribed Image Text:8. Free-radical Cl• atoms can react with ozone in the region of the stratosphere known as the Ozone
Layer, which protects life on Earth from the damaging UV-B and UV-C radiation bands. Use
information this proposed mechanism for that process to answer the questions that follow:
Cl(g) + 03(g) → CIO(g) + O,(g)
(b) Lewis Struct. of ClO:
:C1: 0:
CIO(g) + O3(g) → Cl(g) +2 O,(g)
Cilg)+203(9)+CI0(9)
Overall:
> CID1S)+30zlg)+CIlg)
AH =-285 kJ/moln
203(9)30219)
(a) Write the overall reaction being proposed in the space provided above.
(b)Draw a valid Lewis structure for the ClO molecule in the box, considering electronegativity while placing the
unpaired electron.
(c) Identify any intermediates and/or catalysts:
Intermediate: CIO
Catalyst:CI
(d) Write the rate law assuming the first step is the rate determining step (the REAL MECHANISM):
(e) Write the rate law assuming, incorrectly, that the second step is the rate determining step:
(f) Circle the diagram below that best represents the REAL mechanism, and briefly explain why you chose it.
Reaction Progress
Reaction Progress
(g) A general form of the reaction is shown below.
Propose another element that could stand in for X and say
why you chose it. (~10
WOL)
X+03 → XO + O2
XO + 03 X +202
203→ 3 02
Reaction Progress
Reaction Progress
Energy
Energy
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning