Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Andrei Straumanis
Chapter5: Resonance
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12E
Related questions
Question
Answer for the last question number 9, Thank you. No need for long explanation.
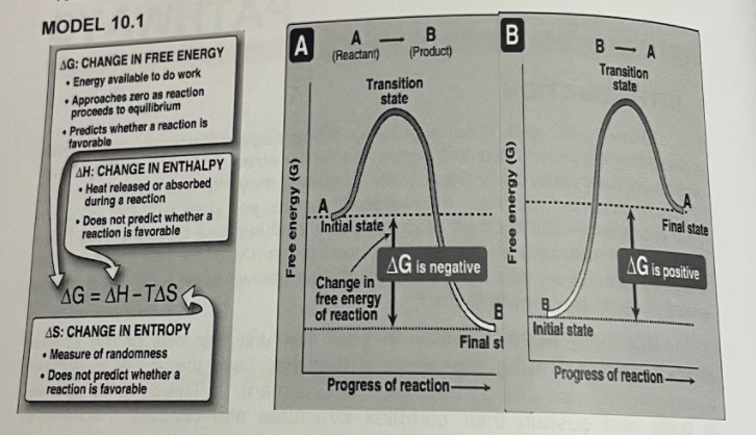
Transcribed Image Text:MODEL 10.1
A
(Reactant)
-
B- A
AG: CHANGE IN FREE ENERGY
Energy available to do work
Approaches zero as reaction
proceeds to equillibrium
• Predicts whether a reaction is
favorable
(Product)
Transition
state
Transition
state
AH: CHANGE IN ENTHALPY
• Heat released or absorbed
during a reaction
• Does not predict whether a
reaction is favorable
A
Initial state
Final state
AG is negative
AG is positive
Change in
free energy
of reaction
AG = AH-TAS
%3D
AS: CHANGE IN ENTROPY
Initial state
Final st
Measure of randomness
• Does not predict whether a
reaction is favorable
Progress of reaction-
Progress of reaction–
B
(5) KBJoue 00
Free energy (G)

Transcribed Image Text:Name:
Date:
Year/Section:
Score:
ACTIVITY 10.1
Refer to Model 10. 1 and answer the question that follows
1. What is free energy? What is its symbol?
2. For an exergonic reaction, what is the value of AG?
3. For an endergonic, what is the value of AG?
4. What are the factors that affect AG?
5. What is energy coupling? In a coupling reaction, what must be the
overall value of AG?
6. What does the cell do with the energy produced from exergonic
reactions?
7. What molecule does the cell use as an energy carrier? Draw its
structure.
8. Why is it that this energy carrier is considered to be high energy
containing phosphate?
9. Bond of this energy carrier of cells is broken through what?
212 Copyright 2019. All Rights Reserved.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning