A 2-kg car initially moving at 6 m/s at a height of 4 m encounters a hill of height 5 m, as shown in Figure. At a later point there is a horizontal spring (with a spring constant k=150 N/m) at a height of 2 m. (a) Does the car reach the spring? (Hint: Compare the initial total mechanical energy of the car with its potential energy at hill of height 5 m) (b) If so, what is the maximum compression in the spring? Ignore frictional losses and the rotational energy of the wheels. g=9.8 m/s2
A 2-kg car initially moving at 6 m/s at a height of 4 m encounters a hill of height 5 m, as shown in Figure. At a later point there is a horizontal spring (with a spring constant k=150 N/m) at a height of 2 m. (a) Does the car reach the spring? (Hint: Compare the initial total mechanical energy of the car with its potential energy at hill of height 5 m) (b) If so, what is the maximum compression in the spring? Ignore frictional losses and the rotational energy of the wheels. g=9.8 m/s2
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Chapter8: Centroids And Distributed Loads
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8.86P: Determine the volume of the concrete arch dam.
Related questions
Question
A 2-kg car initially moving at 6 m/s at a height of 4 m encounters a hill of height 5 m, as shown in Figure. At a later point there is a horizontal spring (with a spring constant k=150 N/m) at a height of 2 m. (a) Does the car reach the spring? (Hint: Compare the initial total
g=9.8 m/s2
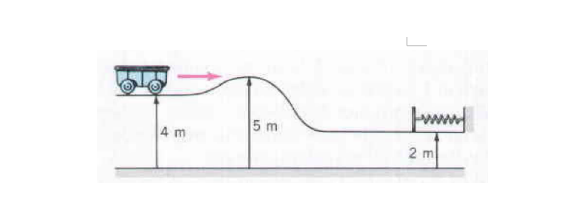
Transcribed Image Text:5 m
2 m
4 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L