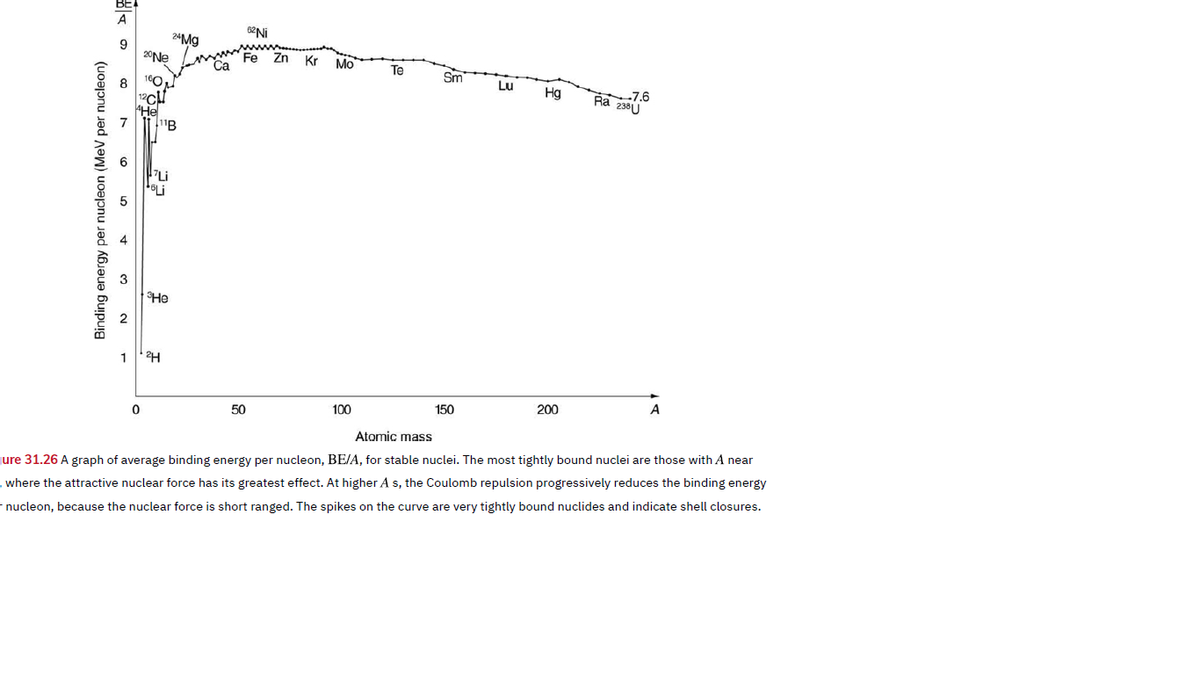
A 24Mg 20Ne Kr Mo Te Sm Lu 7.6 Ra 238U 160 Hg 8 12CH He 7 SHe 1 A 150 200 100 50 Atomic mass jure 31.26 A graph of average binding energy per nucleon, BE/A, for stable nuclei. The most tightly bound nuclei are those with A near where the attractive nuclear force has its greatest effect. At higher A s, the Coulomb repulsion progressively reduces the binding energy r nucleon, because the nuclear force is short ranged. The spikes on the curve are very tightly bound nuclides and indicate shell closures. Binding energy per nucleon (MeV per nucleon)
Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion is a type of nuclear reaction. In nuclear fusion, two or more than two lighter atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus. During this process, an enormous amount of energy is released. This energy is called nuclear energy. Nuclear fusion is the energy source of the sun and stars.
Fusion Bomb
A fusion bomb is also known as a thermonuclear bomb or hydrogen bomb which releases a large amount of explosive energy during a nuclear chain reaction when the lighter nuclei in it, combine to form heavier nuclei, and a large amount of radiation is released. It is an uncontrolled, self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction where isotopes of hydrogen combine under very high temperature to form helium. They work on the principle of operation of atomic fusion. The isotopes of Hydrogen are deuterium and tritium, where they combine their masses and have greater mass than the product nuclei, get heated at high temperatures, and releases energy.
56Fe is among the most tightly bound of all nuclides. It is more than 90% of natural iron. Note that 56Fe has even numbers of both protons and neutrons. Calculate BE/A, the binding energy per nucleon, for 56Fe and compare it with the approximate value obtained from the graph in Figure 31.26.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 8 images









