A 600 KVA generator with X"a = 0.22 per unit is connected to a bus through a circuit breaker, as shown in the following figure. Connected through circuit breakers to the same bus are three synchronous motors rated 200 KVA, 2.5 KV, 1.0 power factor, with X"a = 0.15 per unit. The motors are operating at full load, unity power factor and rated voltage, with the load equally divided among the machines. (a) Find the rated symmetrical short-circuit current in Amperes, which must be interrupting breakers A and B for a fault at point P. Simplify the calculations by neglecting the Prefault current. M. A B M
A 600 KVA generator with X"a = 0.22 per unit is connected to a bus through a circuit breaker, as shown in the following figure. Connected through circuit breakers to the same bus are three synchronous motors rated 200 KVA, 2.5 KV, 1.0 power factor, with X"a = 0.15 per unit. The motors are operating at full load, unity power factor and rated voltage, with the load equally divided among the machines. (a) Find the rated symmetrical short-circuit current in Amperes, which must be interrupting breakers A and B for a fault at point P. Simplify the calculations by neglecting the Prefault current. M. A B M
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305632134
Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Chapter7: Symmetrical Faults
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.8P
Related questions
Question
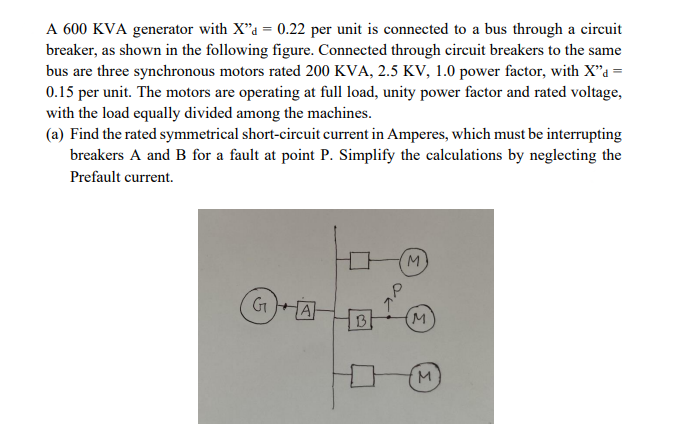
Transcribed Image Text:A 600 KVA generator with X"a = 0.22 per unit is connected to a bus through a circuit
breaker, as shown in the following figure. Connected through circuit breakers to the same
bus are three synchronous motors rated 200 KVA, 2.5 KV, 1.0 power factor, with X"a =
0.15 per unit. The motors are operating at full load, unity power factor and rated voltage,
with the load equally divided among the machines.
(a) Find the rated symmetrical short-circuit current in Amperes, which must be interrupting
breakers A and B for a fault at point P. Simplify the calculations by neglecting the
Prefault current.
M.
GHA
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course …
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305632134
Author:
J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course …
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305632134
Author:
J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:
Cengage Learning