A beaker with 130x10 mL of an acetic acid butter with a pH of 5.000 is sitting on a benchtop. The total molarity of acid and conjugate base in this buffer is 0.100 M. A student adds 8.10 mil. of a 0.460 MHCI solution to the beaker How much will the pH change? The pk, of acetic acid is 4.740 Express your answer numerically to two decimal places. Use a minus (-) sign if the pit has decreased. View Available Hint(s) ApH- Submit AI- ΑΣΦ ProA -8? X Incorrect; Try Again; 6 attempts remaining
A beaker with 130x10 mL of an acetic acid butter with a pH of 5.000 is sitting on a benchtop. The total molarity of acid and conjugate base in this buffer is 0.100 M. A student adds 8.10 mil. of a 0.460 MHCI solution to the beaker How much will the pH change? The pk, of acetic acid is 4.740 Express your answer numerically to two decimal places. Use a minus (-) sign if the pit has decreased. View Available Hint(s) ApH- Submit AI- ΑΣΦ ProA -8? X Incorrect; Try Again; 6 attempts remaining
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Andrei Straumanis
Chapter20: Acidity And Pka Of Phenols
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3CTQ
Related questions
Question
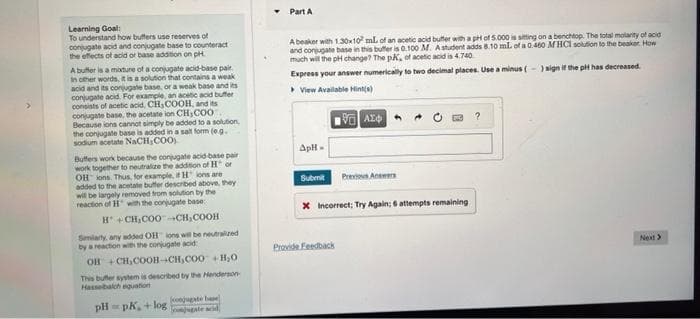
Transcribed Image Text:Learning Goal:
To understand how buffers use reserves of
conjugate acid and conjugate base to counteract
the effects of acid or base addition on pH.
A buffer is a mixture of a conjugate acid-base pair
In other words, it is a solution that contains a weak
acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its
conjugate acid. For example, an acetic acid buffer
consists of acetic acid, CH₂COOH, and its
conjugate base, the acetate ion CH,COO
Because ions cannot simply be added to a solution,
the conjugate base is added in a salt form (e.g.
sodium acetate NaCH₂COO)
Buffers work because the conjugate acid-base pair
work together to neutralize the addition of Hor
OH ions. Thus, for example, it Hions are
added to the acetate buffer described above, they
will be largely removed from solution by the
reaction of H with the conjugate base:
H+CH₂COO-CH₂COOH
Similarly, any added OH ions will be neutralized
by a reaction with the conjugate acid
OH +CH₂COOH-CH₂COO+H₂O
This butter system is described by the Henderson-
Hasselbalch equation
pH=pK, +loggate ad
conjugate base
Part A
A beaker with 1.30x10 mL of an acetic acid butter with a pH of 5.000 is sitting on a benchtop. The total molarity of acid
and conjugate base in this buffer is 0.100 M. A student adds 8.10 mL of a 0.460 M HCl solution to the beaker How
much will the pH change? The pK, of acetic acid is 4.740
Express your answer numerically to two decimal places. Use a minus (-) sign if the pH has decreased.
View Available Hint(s)
ApH-
VAL
Submit Previous Answers
X Incorrect; Try Again; 6 attempts remaining
Provide Feedback
?
Next >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
