A biochemical engineer isolates a bacterial gene fragment and dissolves a 11.5-mg sample in enough water to make 30.0 ml. of solution. The osmotic pressure of the solution is 0.340 torr at 25.0 °C. Assume the gene fragment does not dissociate into multiple ions when added to the solution. Be sure each of your answer entries has the correct number of significant figures.. Note: Reference the Conversion factors for non-SI units table for additional information. Note: Reference the Fundamental constants table for additional information. Note: Reference the Molal freezing point depression and boiling point elevation constants table for additional information. Part 1 of 2 What is the molar mass of the gene fragment? Part 2 of 2 If the solution density is 0.997 how large is the freezing point depression for this solution? D.P ml.
A biochemical engineer isolates a bacterial gene fragment and dissolves a 11.5-mg sample in enough water to make 30.0 ml. of solution. The osmotic pressure of the solution is 0.340 torr at 25.0 °C. Assume the gene fragment does not dissociate into multiple ions when added to the solution. Be sure each of your answer entries has the correct number of significant figures.. Note: Reference the Conversion factors for non-SI units table for additional information. Note: Reference the Fundamental constants table for additional information. Note: Reference the Molal freezing point depression and boiling point elevation constants table for additional information. Part 1 of 2 What is the molar mass of the gene fragment? Part 2 of 2 If the solution density is 0.997 how large is the freezing point depression for this solution? D.P ml.
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
7th Edition
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:H. Stephen Stoker
Chapter8: Solutions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8.113EP: Consider two solutions, A and B, separated by an osmotic semipermeable membrane that allows only...
Related questions
Question
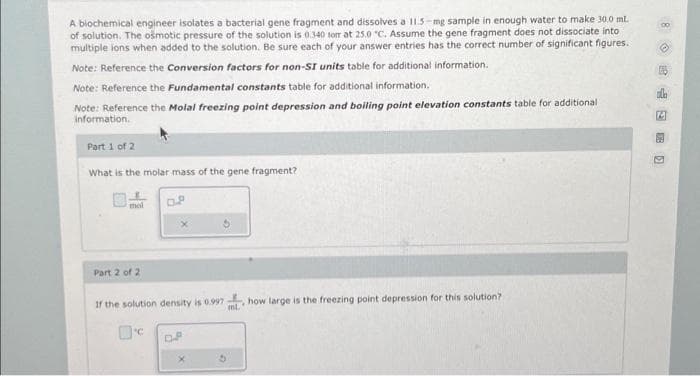
Transcribed Image Text:A biochemical engineer isolates a bacterial gene fragment and dissolves a 11.5-mg sample in enough water to make 30.0 mL.
of solution. The osmotic pressure of the solution is 0.340 torr at 25.0 "C. Assume the gene fragment does not dissociate into
multiple ions when added to the solution. Be sure each of your answer entries has the correct number of significant figures.
Note: Reference the Conversion factors for non-SI units table for additional information.
Note: Reference the fundamental constants table for additional information.
Note: Reference the Molal freezing point depression and boiling point elevation constants table for additional
information.
Part 1 of 2
What is the molar mass of the gene fragment?
mal
Part 2 of 2
0.8
If the solution density is 0.997 how large is the freezing point depression for this solution?
ml.
'C
D.P
G
ala
14
E
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 12 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285853918
Author:
H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285853918
Author:
H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning