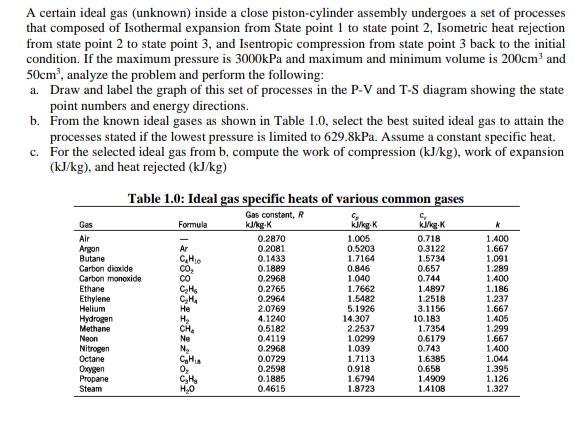
A certain ideal gas (unknown) inside a close piston-cylinder assembly undergoes a set of processes that composed of Isothermal expansion from State point 1 to state point 2, Isometric heat rejection from state point 2 to state point 3, and Isentropic compression from state point 3 back to the initial condition. If the maximum pressure is 3000kPa and maximum and minimum volume is 200cm and 50cm', analyze the problem and perform the following: a. Draw and label the graph of this set of processes in the P-V and T-S diagram showing the state point numbers and energy directions. b. From the known ideal gases as shown in Table 1.0, select the best suited ideal gas to attain the processes stated if the lowest pressure is limited to 629.8kPa. Assume a constant specific heat. c. For the selected ideal gas from b, compute the work of compression (kJ/kg), work of expansion (kJ/kg), and heat rejected (kJ/kg) Table 1.0: Ideal gas specific heats of various common gases Gas constant, R kgK Gas Formula 0.718 0.3122 1.5734 0.657 0.744 14897 1.2518 3.1156 10.183 1.7354 0.6179 0.743 1.6385 0.658 14909 14108 Air 0.2870 1.005 0.5203 1.7164 0.846 1.040 1.7662 1.5482 5.1926 14.307 2.2537 1.0299 1.039 1.7113 0.918 1.6794 1.8723 1.400 1.667 1.091 1.289 1.400 1.186 1.237 1.667 1.405 1.299 1.667 1.400 1.044 0.2081 0.1433 0.1889 0.2968 0.2765 0.2964 Argon Butane Carbon diaxide Carbon monoxide Ethane Ethylene Helium 2.0769 4.1240 0.5182 0.4119 0.2968 0.0729 0.2598 0.1885 0.4615 Hydrogen Methane Neon Nitrogen Octane Onygen Propane Steam 1.395 1.126 1.327
Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements
Measurement is a term that refers to analyzing a manufactured component regarding the degree of accuracy for dimensions, tolerances, geometric profile, roundness, flatness, smoothness, etc. Measurement always involves comparing the manufactured component or the prototype with a standard specimen whose dimensions and other parameters are assumed to be perfect and do not undergo changes with respect to time.Precisely in mechanical engineering the branch that deals with the application of scientific principles for measurements is known as metrology. The domain of metrology in general deals with various measurements like mechanical, chemical, thermodynamic, physical, and biological measurements. In mechanical engineering, the measurements are limited to mechanical specific such as length, mass, surface profile, flatness, roundness, viscosity, heat transfer, etc.
Basic principles of engineering metrology
Metrology is described as the science of measurement, precision, and accuracy. In other words, it is a method of measurement based on units and predefined standards.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps


