A company manufactures particle boards in a production facility. With recent increases in input costs, the company has implemented new machines that lower raw material waste and reduce en- ergy consumption. The new machines also have improved automation and therefore lower the labour requirements for the same level of production. The company believes that if a 3% improve- ment productivity (with respect to each input) is achieved it will offset the increased raw material costs. The company calculated the following information | LAST YEAR CURRENT YEAR 10,000 Boards produced Labour (hours) Wood chips (kg) Resin (kg) Energy (kWh) Labour cost (S/hour) Wood chips cost (S/kg) Resin (S/kg) Energy (S/kWh) 10,000 15,250 10,150 16,000 10,750 500 470 30,000 28,500 20.00 21.50 15.15 15.35 3.55 3.50 0.09 0.10
A company manufactures particle boards in a production facility. With recent increases in input costs, the company has implemented new machines that lower raw material waste and reduce en- ergy consumption. The new machines also have improved automation and therefore lower the labour requirements for the same level of production. The company believes that if a 3% improve- ment productivity (with respect to each input) is achieved it will offset the increased raw material costs. The company calculated the following information | LAST YEAR CURRENT YEAR 10,000 Boards produced Labour (hours) Wood chips (kg) Resin (kg) Energy (kWh) Labour cost (S/hour) Wood chips cost (S/kg) Resin (S/kg) Energy (S/kWh) 10,000 15,250 10,150 16,000 10,750 500 470 30,000 28,500 20.00 21.50 15.15 15.35 3.55 3.50 0.09 0.10
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter4: Linear Programming Models
Section4.8: Data Envelopment Analysis (dea)
Problem 42P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:a. Evaluate the productivity of boards per each of the four manufacturing inputs (labour, wood
chips, resin and energy) for each year. Do the separate measures indicate a 3% improvement?
b. Evaluate the same productivity measures as in step (a) but in terms of monetary cost. Is the
3% improvement (for each input) still present?
c. Calculate the multi-factor (boards per cost of all inputs) productivity improvement. Is the
ultimate goal of offsetting rises in input costs achieved?
d. A significant investment was made to acquire the new machines. Engineers believe that
further improvements can still be made. In which area (labour use, wood chip or resin waste,
energy usage) should the company concentrate future investment towards improvement?
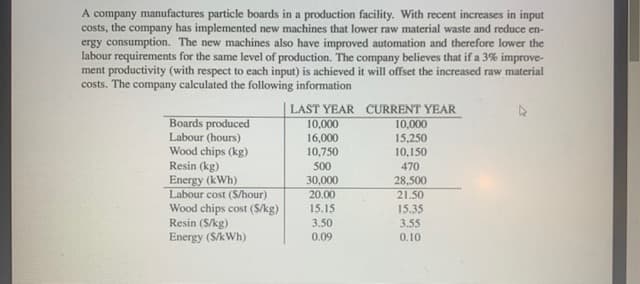
Transcribed Image Text:A company manufactures particle boards in a production facility. With recent increases in input
costs, the company has implemented new machines that lower raw material waste and reduce en-
ergy consumption. The new machines also have improved automation and therefore lower the
labour requirements for the same level of production. The company believes that if a 3% improve-
ment productivity (with respect to each input) is achieved it will offset the increased raw material
costs. The company calculated the following information
|LAST YEAR CURRENT YEAR
10,000
15,250
10,150
Boards produced
Labour (hours)
Wood chips (kg)
Resin (kg)
Energy (kWh)
Labour cost (S/hour)
Wood chips cost (S/kg)
Resin (S/kg)
Energy (S/kWh)
10,000
16,000
10,750
500
470
30,000
28,500
20.00
21.50
15.15
15.35
3.50
3.55
0.09
0.10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, operations-management and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Management, Loose-Leaf Version
Management
ISBN:
9781305969308
Author:
Richard L. Daft
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Management, Loose-Leaf Version
Management
ISBN:
9781305969308
Author:
Richard L. Daft
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub