A conducting rod of length l= 35.0 cm is free to slide on two parallel conducting bars as shown in Figure P30.35. Two resistors R1 =2.00 2 and R2 = 5.00 2 are connected across the ends of the bars to form a loop. A constant magnetic field B= 2.50 T is directed perpendicularly into the page. An external agent pulls the rod to the left with a constant speed of v= 8.00 m/s. Find (a) the currents in both resistors, (b) the total power delivered to the resistance of the circuit, and (c) the magnitude of the applied force that is needed to move the rod with this constant velocity. Figure P30.35 xxx XX x x x x x x
A conducting rod of length l= 35.0 cm is free to slide on two parallel conducting bars as shown in Figure P30.35. Two resistors R1 =2.00 2 and R2 = 5.00 2 are connected across the ends of the bars to form a loop. A constant magnetic field B= 2.50 T is directed perpendicularly into the page. An external agent pulls the rod to the left with a constant speed of v= 8.00 m/s. Find (a) the currents in both resistors, (b) the total power delivered to the resistance of the circuit, and (c) the magnitude of the applied force that is needed to move the rod with this constant velocity. Figure P30.35 xxx XX x x x x x x
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter30: Faraday's Law
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 35AP: A conducting rod of length = 35.0 cm is free to slide on two parallel conducting bars as shown in...
Related questions
Question
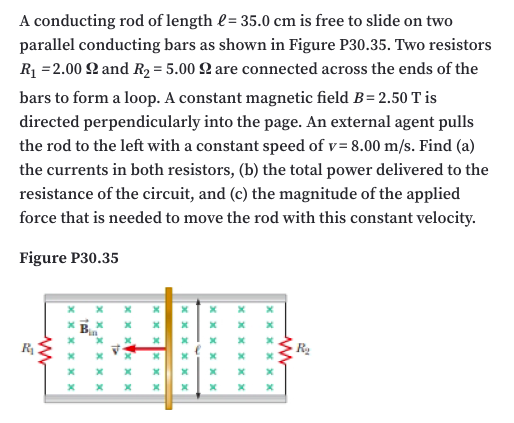
Transcribed Image Text:A conducting rod of length l= 35.0 cm is free to slide on two
parallel conducting bars as shown in Figure P30.35. Two resistors
R =2.00 2 and R2 = 5.00 Q are connected across the ends of the
bars to form a loop. A constant magnetic field B= 2.50 T is
directed perpendicularly into the page. An external agent pulls
the rod to the left with a constant speed of v= 8.00 m/s. Find (a)
the currents in both resistors, (b) the total power delivered to the
resistance of the circuit, and (c) the magnitude of the applied
force that is needed to move the rod with this constant velocity.
Figure P30.35
x x x x x xc
x x x x x x
x x x x x x
X xx x x
x x x
xx
X x x
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning