(a) Consider the following common-source amplifier: VDD = 1.5 V WIL = 5.6 μm / 28 nm HnCox = 400 μA/V² ID,BIAS = 1.25 mA Rs Vin VDD Ţ www. RD HH CD: CD = 200 fF RD = 600 Rs = 102 CGS = 100 fF CDB = 80 fF Ignore channel-length modulation Fig. 1 1. Calculate the low frequency voltage gain. 2. Calculate the input and output poles of Fig. 1 in MHz.
(a) Consider the following common-source amplifier: VDD = 1.5 V WIL = 5.6 μm / 28 nm HnCox = 400 μA/V² ID,BIAS = 1.25 mA Rs Vin VDD Ţ www. RD HH CD: CD = 200 fF RD = 600 Rs = 102 CGS = 100 fF CDB = 80 fF Ignore channel-length modulation Fig. 1 1. Calculate the low frequency voltage gain. 2. Calculate the input and output poles of Fig. 1 in MHz.
Chapter25: Television, Telephone, And Low-voltage Signal Systems
Section25.1: Television Circuit
Problem 5R: From a cost standpoint, which system is more economical to install: a master amplifier distribution...
Related questions
Question
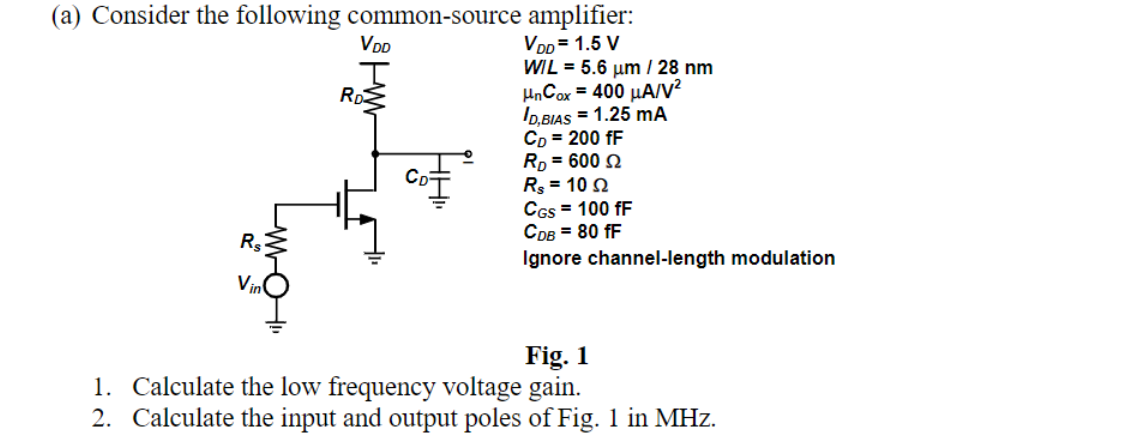
Transcribed Image Text:(a) Consider the following common-source amplifier:
VDD=1.5 V
WIL = 5.6 μm / 28 nm
HnCox = 400 μA/V²
شما
VDD
RD
ID,BIAS = 1.25 mA
CD = 200 fF
RD = 600
Rs = 102
CGS = 100 fF
CDB = 80 fF
Ignore channel-length modulation
Fig. 1
1. Calculate the low frequency voltage gain.
2. Calculate the input and output poles of Fig. 1 in MHz.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

EBK ELECTRICAL WIRING RESIDENTIAL
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337516549
Author:
Simmons
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

EBK ELECTRICAL WIRING RESIDENTIAL
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337516549
Author:
Simmons
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT