A force P pulls on a box of mass m that is in contact with a rough surface. The figure shows the magnitudes and directions of the forces that act on the box in this situation. W represents the weight of the box. Fn represents the normal force on the box, and f represents the frictional force. ... P = 160 N f = 80 N 60° W = 196 N Which statement best describes the motion of the crate? A The box must be moving with constant acceleration. B The box must be moving with constant velocity. © The box may be either at rest or moving with constant velocity. The box may be either at rest or moving with constant acceleration. E) The box must be at rest.
A force P pulls on a box of mass m that is in contact with a rough surface. The figure shows the magnitudes and directions of the forces that act on the box in this situation. W represents the weight of the box. Fn represents the normal force on the box, and f represents the frictional force. ... P = 160 N f = 80 N 60° W = 196 N Which statement best describes the motion of the crate? A The box must be moving with constant acceleration. B The box must be moving with constant velocity. © The box may be either at rest or moving with constant velocity. The box may be either at rest or moving with constant acceleration. E) The box must be at rest.
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Katz, Debora M.
Chapter6: Applications Of Newton’s Laws Of Motion
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5PQ
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
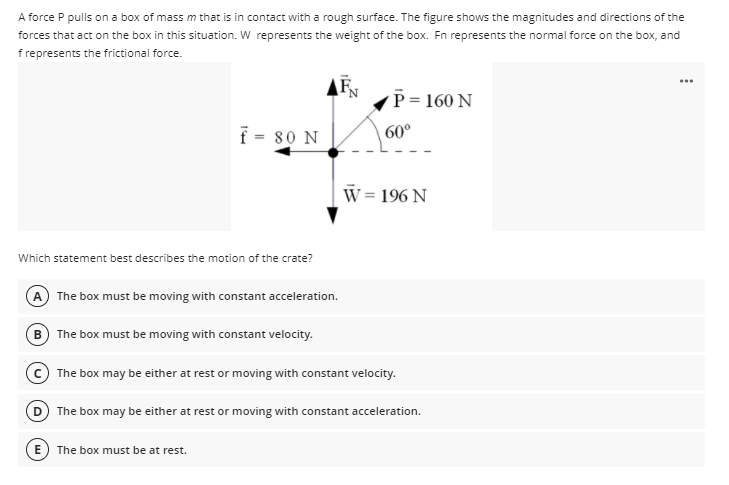
Transcribed Image Text:A force P pulls on a box of mass m that is in contact with a rough surface. The figure shows the magnitudes and directions of the
forces that act on the box in this situation. W represents the weight of the box. Fn represents the normal force on the box, and
f represents the frictional force.
...
P = 160 N
f = 80 N
60°
W= 196 N
Which statement best describes the motion of the crate?
A The box must be moving with constant acceleration.
B The box must be moving with constant velocity.
The box may be either at rest or moving with constant velocity.
D The box may be either at rest or moving with constant acceleration.
The box must be at rest.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University