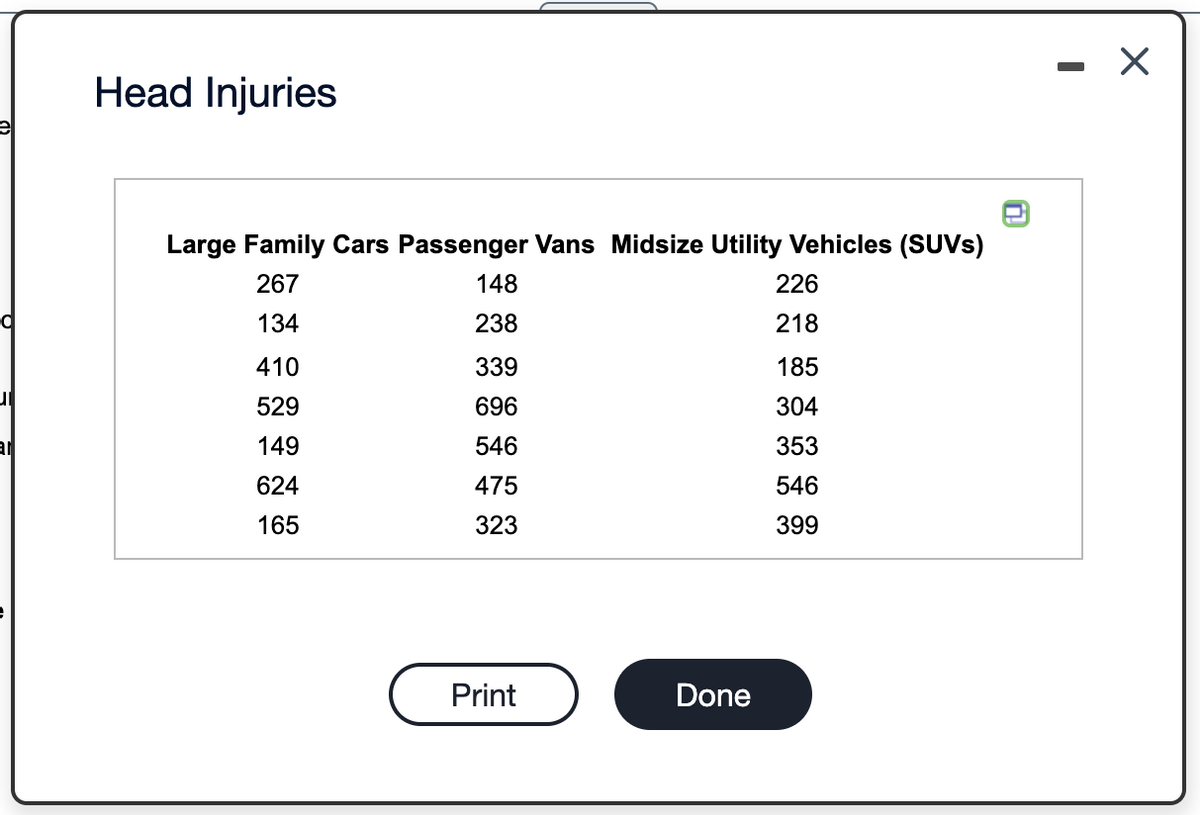
A highway safety institution conducts experiments in which cars are crashed into a fixed barrier at 40 mph. In the institute's 40-mph offset test, 40% of the total width of each vehicle strikes a barrier on the driver's side. The barrier's deformable face is made of aluminum honeycomb, which makes the forces in the test similar to those involved in a frontal offset crash between two vehicles of the same weight, each going just less than 40 mph. You are in the market to buy a family car and you want to know if the mean head injury resulting from this offset crash is the same for large family cars, passenger vans, and midsize utility vehicles (SUVs). The data in the accompanying table were collected from the institute's study. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
Minimization
In mathematics, traditional optimization problems are typically expressed in terms of minimization. When we talk about minimizing or maximizing a function, we refer to the maximum and minimum possible values of that function. This can be expressed in terms of global or local range. The definition of minimization in the thesaurus is the process of reducing something to a small amount, value, or position. Minimization (noun) is an instance of belittling or disparagement.
Maxima and Minima
The extreme points of a function are the maximum and the minimum points of the function. A maximum is attained when the function takes the maximum value and a minimum is attained when the function takes the minimum value.
Derivatives
A derivative means a change. Geometrically it can be represented as a line with some steepness. Imagine climbing a mountain which is very steep and 500 meters high. Is it easier to climb? Definitely not! Suppose walking on the road for 500 meters. Which one would be easier? Walking on the road would be much easier than climbing a mountain.
Concavity
In calculus, concavity is a descriptor of mathematics that tells about the shape of the graph. It is the parameter that helps to estimate the maximum and minimum value of any of the functions and the concave nature using the graphical method. We use the first derivative test and second derivative test to understand the concave behavior of the function.
A highway safety institution conducts experiments in which cars are crashed into a fixed barrier at 40 mph. In the institute's 40-mph offset test, 40% of the total width of each vehicle strikes a barrier on the driver's side. The barrier's deformable face is made of aluminum honeycomb, which makes the forces in the test similar to those involved in a frontal offset crash between two vehicles of the same weight, each going just less than 40 mph. You are in the market to buy a family car and you want to know if the mean head injury resulting from this offset crash is the same for large family cars, passenger vans, and midsize utility vehicles (SUVs). The data in the accompanying table were collected from the institute's study. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images


