A large plane wall is subjected to specified heat flux and temperature on the left surface and no conditions on the right surface. The mathematical formulation, the variation of temperature in the plate, and the right surface temperature are to be determined for steady one-dimensional heat transfer. k=2.5 W/m-°C. k =700 W/m? Tj=80°C L=0.3 m
A large plane wall is subjected to specified heat flux and temperature on the left surface and no conditions on the right surface. The mathematical formulation, the variation of temperature in the plate, and the right surface temperature are to be determined for steady one-dimensional heat transfer. k=2.5 W/m-°C. k =700 W/m? Tj=80°C L=0.3 m
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter2: Steady Heat Conduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2.21P
Related questions
Question
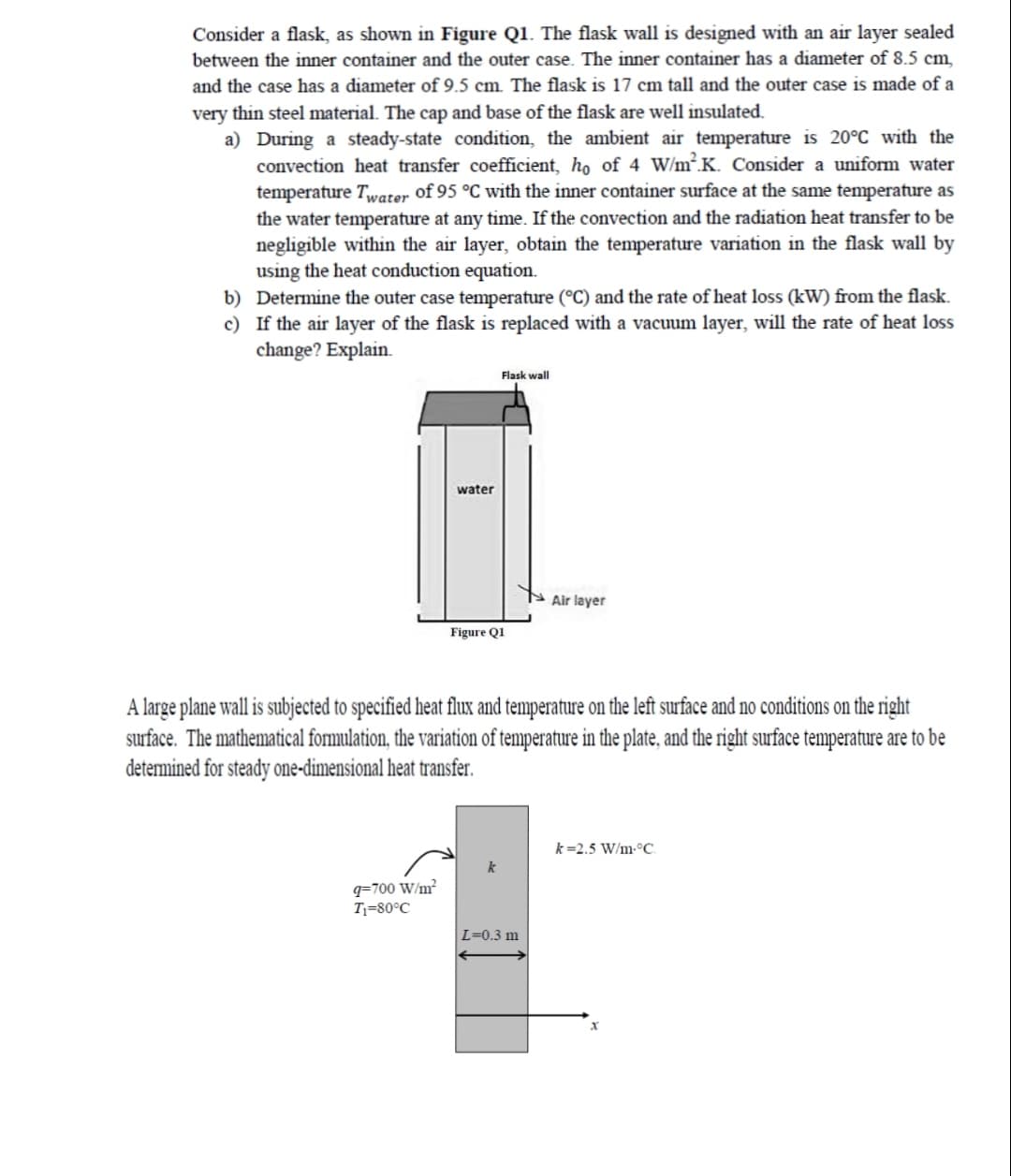
Transcribed Image Text:Consider a flask, as shown in Figure Q1. The flask wall is designed with an air layer sealed
between the inner container and the outer case. The inner container has a diameter of 8.5 cm,
and the case has a diameter of 9.5 cm. The flask is 17 cm tall and the outer case is made of a
very thin steel material. The cap and base of the flask are well insulated.
a) During a steady-state condition, the ambient air temperature is 20°C with the
convection heat transfer coefficient, ho of 4 W/m².K. Consider a uniform water
temperature Twater of 95 °C with the inner container surface at the same temperature as
the water temperature at any time. If the convection and the radiation heat transfer to be
negligible within the air layer, obtain the temperature variation in the flask wall by
using the heat conduction equation.
b) Determine the outer case temperature (°C) and the rate of heat loss (kW) from the flask.
c) If the air layer of the flask is replaced with a vacuum layer, will the rate of heat loss
change? Explain.
Flask wall
water
Air layer
Figure Q1
A large plane wall is subjected to specified heat flux and temperature on the left surface and no conditions on the right
surface. The mathematical formulation, the variation of temperature in the plate, and the right surface temperature are to be
determined for steady one-dimensional heat transfer.
k=2.5 W/m-°C.
q=700 W/m²
T;=80°C
L=0.3 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning