A light spring with force constant 3.00 N/m is compressed by 7.60 cm as it is held between a 0.300-kg block on the left and a 0.600-kg block on the right, both resting on a horizontal surface. The spring exerts a force on each block, tending to push the blocks apart. The blocks are simultaneously released from rest. Find the acceleration with which each block starts to move, given that the coefficient of kinetic friction between each block and the surface is 0, 0.052, and 0.414. (Let the coordinate system be positive to the right and negative to the left. Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer. Assume that the coefficient of static friction is the same as the coefficient of kinetic friction. If the block does not move, enter 0.) (a) u = 0 heavier block Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m/s2 lighter block Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m/s? (b) H = 0.052 heavier block m/s2 m/s² lighter block (c) με 0.414 heavier block m/s2 m/s² lighter block
A light spring with force constant 3.00 N/m is compressed by 7.60 cm as it is held between a 0.300-kg block on the left and a 0.600-kg block on the right, both resting on a horizontal surface. The spring exerts a force on each block, tending to push the blocks apart. The blocks are simultaneously released from rest. Find the acceleration with which each block starts to move, given that the coefficient of kinetic friction between each block and the surface is 0, 0.052, and 0.414. (Let the coordinate system be positive to the right and negative to the left. Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer. Assume that the coefficient of static friction is the same as the coefficient of kinetic friction. If the block does not move, enter 0.) (a) u = 0 heavier block Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m/s2 lighter block Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m/s? (b) H = 0.052 heavier block m/s2 m/s² lighter block (c) με 0.414 heavier block m/s2 m/s² lighter block
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter6: Energy Of A System
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 26P
Related questions
Question
Question in pic.
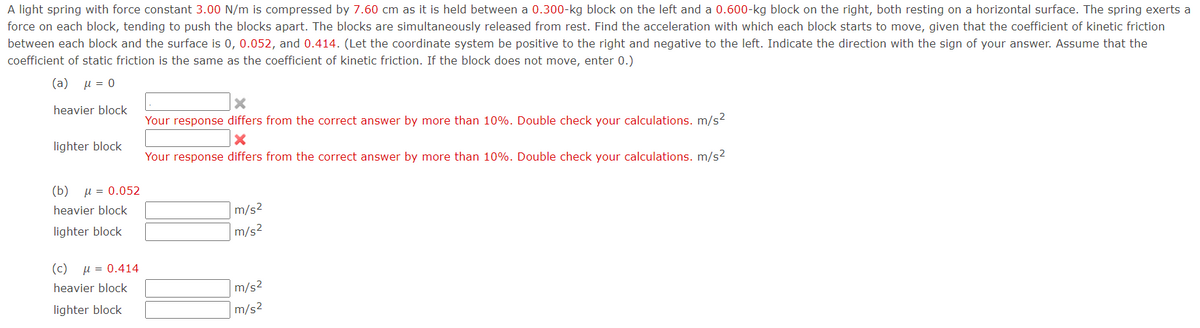
Transcribed Image Text:A light spring with force constant 3.00 N/m is compressed by 7.60 cm as it is held between a 0.300-kg block on the left and a 0.600-kg block on the right, both resting on a horizontal surface. The spring exerts a
force on each block, tending to push the blocks apart. The blocks are simultaneously released from rest. Find the acceleration with which each block starts to move, given that the coefficient of kinetic friction
between each block and the surface is 0, 0.052, and 0.414. (Let the coordinate system be positive to the right and negative to the left. Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer. Assume that the
coefficient of static friction is the same as the coefficient of kinetic friction. If the block does not move, enter 0.)
( a) μ=0
heavier block
Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m/s2
lighter block
Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m/s2
(b)
u = 0.052
heavier block
m/s2
lighter block
m/s2
(c)
u = 0.414
heavier block
m/s2
lighter block
m/s2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:
9780534408961
Author:
Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning