A nonconducting, thin plane sheet of charge carries a uniform charge per unit area of 6.25 μC/m2 as in the figure below. Gaussian surface Gaussian (a) Find the electric field at a distance of 9.12 cm from the plate
A nonconducting, thin plane sheet of charge carries a uniform charge per unit area of 6.25 μC/m2 as in the figure below. Gaussian surface Gaussian (a) Find the electric field at a distance of 9.12 cm from the plate
College Physics
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter15: Electric Forces And Electric Fields
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 56AP: A nonconducting, thin plane sheet of charge carries a uniform charge per unit area of 5.20 C/m2 as...
Related questions
Question
100%
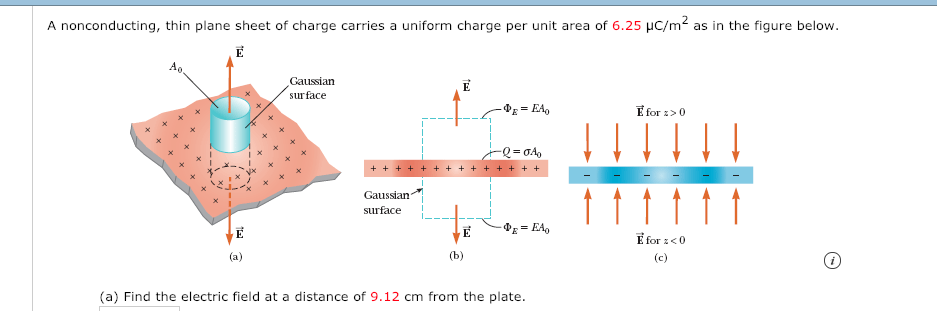
Transcribed Image Text:A nonconducting, thin plane sheet of charge carries a uniform charge per unit area of 6.25 μC/m2 as in the figure below.
Gaussian
surface
Gaussian
(a) Find the electric field at a distance of 9.12 cm from the plate
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning