A person's body mass index (BMI) is computed by dividing the weight (kg) by the square of height (m). The accompanying table contains the BMI statistics for random samples of males and females. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Let population 1 be females. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. E Click the icon to view the table of statistics. OC. Ho: =2 H, H2 H, =P2 OD. Ho H1
A person's body mass index (BMI) is computed by dividing the weight (kg) by the square of height (m). The accompanying table contains the BMI statistics for random samples of males and females. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Let population 1 be females. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. E Click the icon to view the table of statistics. OC. Ho: =2 H, H2 H, =P2 OD. Ho H1
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.4: Distributions Of Data
Problem 19PFA
Related questions
Question
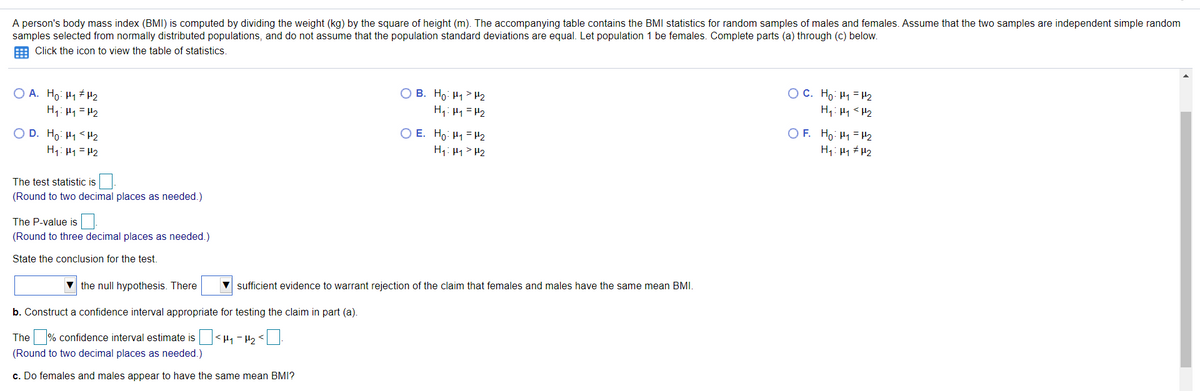
Transcribed Image Text:A person's body mass index (BMI) is computed by dividing the weight (kg) by the square of height (m). The accompanying table contains the BMI statistics for random samples of males and females. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random
samples selected from normally distributed populations, and do not assume that the population standard deviations are equal. Let population 1 be females. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
E Click the icon to view the table of statistics.
O A. Ho: H1 # H2
H1: H4 = H2
O C. Ho: H1 = H2
O B. Ho: H1> H2
H: H1 =H2
O E. Ho: H1 = H2
H: H1> H2
O F. Ho: H1 =H2
O D. Ho: H1 <H2
H1: H1= H2
H1: H1 # H2
The test statistic is
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
The P-value is
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
State the conclusion for the test.
the null hypothesis. There
sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that females and males have the same mean BMI.
b. Construct a confidence interval appropriate for testing the claim in part (a).
The % confidence interval estimate is <H1 - H2 <
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
c. Do females and males appear to have the same mean BMI?
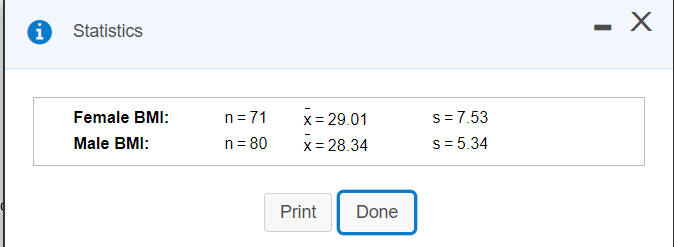
Transcribed Image Text:Statistics
n=71
x = 29.01
x= 28.34
Female BMI:
s=7.53
Male BMI:
n = 80
s= 5.34
Print
Done
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill