A police department released the numbers of calls for the different days of the week during the month of October, as shown in the table to the right. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the different days of the week have the same frequencies of police calls. What is the fundamental error with this analysis? Sun Mon Tues Fri Sat D Day Frequency Wed 246 Thurs 172 160 210 227 208 234 Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho: H₁: Calculate the test statistic, x². x² = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Calculate the P-value. P-value = (Round to four decimal places as needed.) What is the conclusion for this hypothesis test? O A. Reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the different days of the week have the same frequencies of police calls. O B. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the different days of the week have the same frequencies of police calls. OC. Fail to reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the different days of the week have the same frequencies of police calls. O D. Fail to reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the different days of the week have the same frequencies of police calls. What is the fundamental error with this analysis? O A. Because October has 31 days, each day of the week occurs the same number of times as the other days of the week. O B. Because October has 31 days, three of the days of the week occur more often than the other days of the week. O C. Because October has 31 days, two of the days of the week occur more often than the other days of the week. O D. Because October has 31 days, one of the days of the week occur more often than the other days of the week.
A police department released the numbers of calls for the different days of the week during the month of October, as shown in the table to the right. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that the different days of the week have the same frequencies of police calls. What is the fundamental error with this analysis? Sun Mon Tues Fri Sat D Day Frequency Wed 246 Thurs 172 160 210 227 208 234 Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho: H₁: Calculate the test statistic, x². x² = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Calculate the P-value. P-value = (Round to four decimal places as needed.) What is the conclusion for this hypothesis test? O A. Reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the different days of the week have the same frequencies of police calls. O B. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the different days of the week have the same frequencies of police calls. OC. Fail to reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the different days of the week have the same frequencies of police calls. O D. Fail to reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the different days of the week have the same frequencies of police calls. What is the fundamental error with this analysis? O A. Because October has 31 days, each day of the week occurs the same number of times as the other days of the week. O B. Because October has 31 days, three of the days of the week occur more often than the other days of the week. O C. Because October has 31 days, two of the days of the week occur more often than the other days of the week. O D. Because October has 31 days, one of the days of the week occur more often than the other days of the week.
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13PT
Related questions
Question
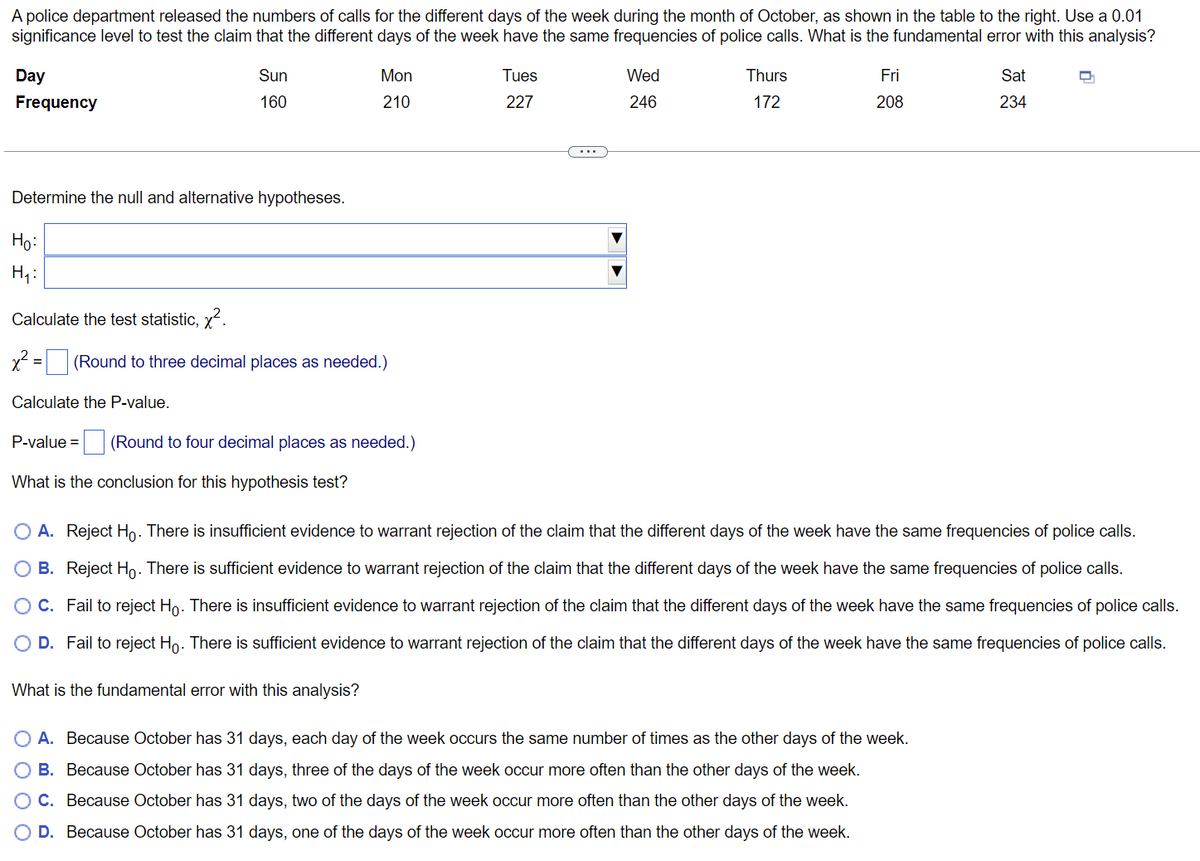
Transcribed Image Text:A police department released the numbers of calls for the different days of the week during the month of October, as shown in the table to the right. Use a 0.01
significance level to test the claim that the different days of the week have the same frequencies of police calls. What is the fundamental error with this analysis?
Sun
Mon
Tues
Wed
Thurs
Fri
Sat
Day
Frequency
160
210
227
246
172
208
234
Determine the null and alternative hypotheses.
Ho:
H₁:
Calculate the test statistic, x².
x² = (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Calculate the P-value.
P-value =
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
What is the conclusion for this hypothesis test?
O A. Reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the different days of the week have the same frequencies of police calls.
B. Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the different days of the week have the same frequencies of police calls.
C. Fail to reject Hỏ. There is insufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the different days of the week have the same frequencies of police calls.
O D. Fail to reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the different days of the week have the same frequencies of police calls.
What is the fundamental error with this analysis?
O A. Because October has 31 days, each day of the week occurs the same number of times as the other days of the week.
B. Because October has 31 days, three of the days of the week occur more often than the other days of the week.
O C. Because October has 31 days, two of the days of the week occur more often than the other days of the week.
D. Because October has 31 days, one of the days of the week occur more often than the other days of the week.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL