A rotating viscometer consists of two concentric cylinders-a stationary inner cylinder of radius R, and an outer cylinder of inside radius Ro rotating at angular velocity (rotation rate) wo. In the tiny gap between the two cylinders is the fluid whose viscosity (u) is to be measured. The length of the cylinders (into the page in Figure 1) is L. L is large such that end effects are negligible (we can treat this as a two-dimensional problem). Torque (T) is required to rotate the outer cylinder at constant speed. Showing all your work and algebra, generate an approximate expression of T as a function of the other variables. Liquid: p, H. R₂ Stationary inner cylinder Rotating outer cylinder
A rotating viscometer consists of two concentric cylinders-a stationary inner cylinder of radius R, and an outer cylinder of inside radius Ro rotating at angular velocity (rotation rate) wo. In the tiny gap between the two cylinders is the fluid whose viscosity (u) is to be measured. The length of the cylinders (into the page in Figure 1) is L. L is large such that end effects are negligible (we can treat this as a two-dimensional problem). Torque (T) is required to rotate the outer cylinder at constant speed. Showing all your work and algebra, generate an approximate expression of T as a function of the other variables. Liquid: p, H. R₂ Stationary inner cylinder Rotating outer cylinder
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305578296
Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Chapter11: Calibrating Instruments
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4RQ: Temperature-measuring instruments may be designed to measure the temperature of vapors, ________,...
Related questions
Question
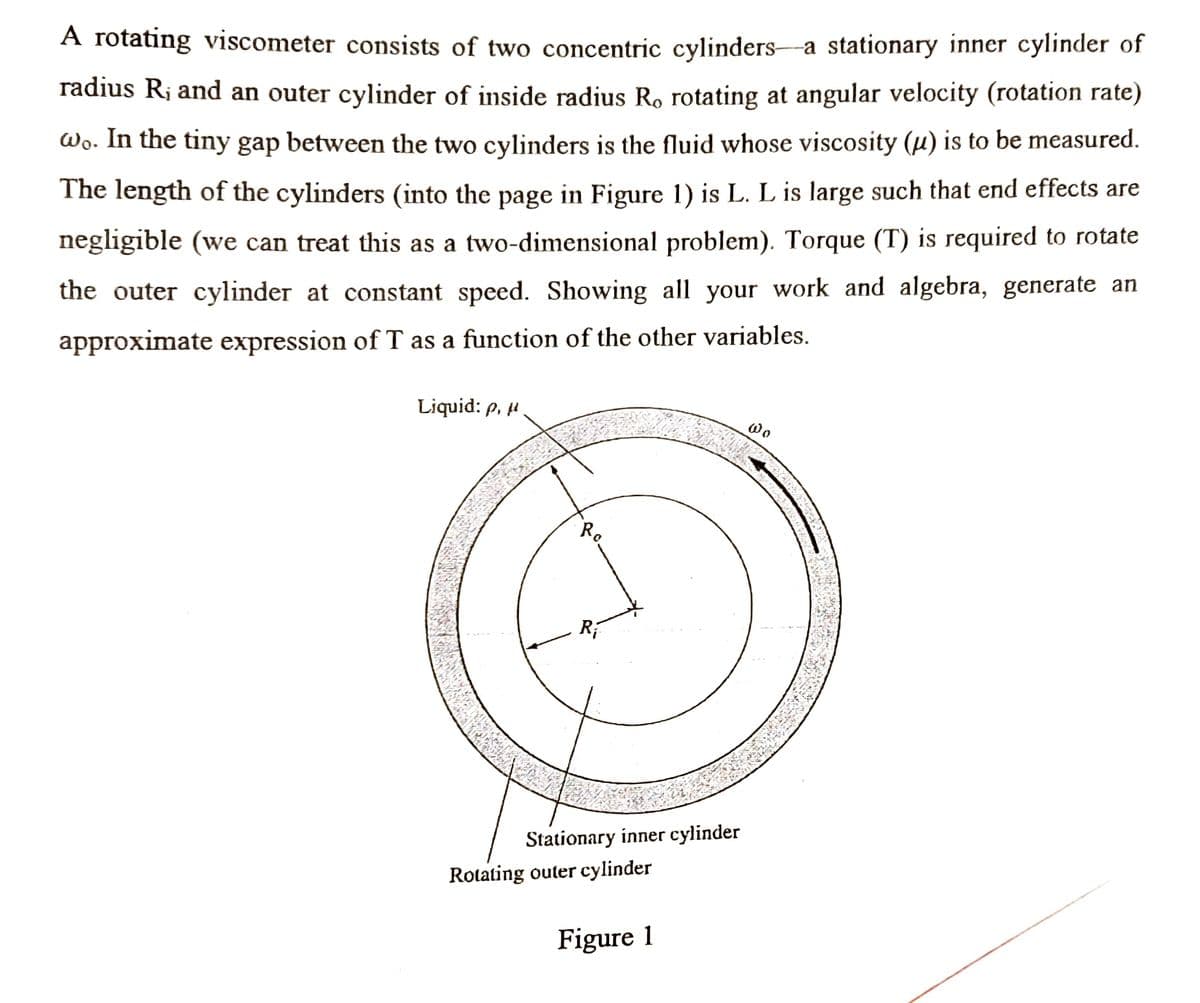
Transcribed Image Text:A rotating viscometer consists of two concentric cylinders-a stationary inner cylinder of
radius R, and an outer cylinder of inside radius Ro rotating at angular velocity (rotation rate)
wo. In the tiny gap between the two cylinders is the fluid whose viscosity (u) is to be measured.
The length of the cylinders (into the page in Figure 1) is L. L is large such that end effects are
negligible (we can treat this as a two-dimensional problem). Torque (T) is required to rotate
the outer cylinder at constant speed. Showing all your work and algebra, generate an
approximate expression of T as a function of the other variables.
Liquid: p,
Ro
Ri
Stationary inner cylinder
Rotating outer cylinder
Figure 1
Wo
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning