A sample of 500 respondents was selected in a large metropolitan area to study consumer behavior. The resulting contingency table is shown to the Enjoys shopping for clothing right. Complete parts (a) through (c). Gender Female 222 Total 353 Male Yes 131 No 107 40 147 Total 238 262 500 a. Suppose the respondent chosen is a female. What is the probability that she does not enjoy shopping for clothing? P(does not enjoy shopping|female) =O (Round to four decimal places as needed.) b. Suppose the respondent chosen enjoys shopping for clothing. What is the probability that the individual is a male? P(maleļenjoys shopping) = (Round to four decimal places as needed.) c. Are enjoying shopping for clothing and the gender of the individual statistically independent? Explain. O A. Yes, because P(malelenjoys shopping) = P(male). B. No, because P(male|enjoys shopping) = P(male). Oc. Yes, because P(malelenjoys shopping) + P(male). O D. No, because P(malelenjoys shopping) # P(male).
A sample of 500 respondents was selected in a large metropolitan area to study consumer behavior. The resulting contingency table is shown to the Enjoys shopping for clothing right. Complete parts (a) through (c). Gender Female 222 Total 353 Male Yes 131 No 107 40 147 Total 238 262 500 a. Suppose the respondent chosen is a female. What is the probability that she does not enjoy shopping for clothing? P(does not enjoy shopping|female) =O (Round to four decimal places as needed.) b. Suppose the respondent chosen enjoys shopping for clothing. What is the probability that the individual is a male? P(maleļenjoys shopping) = (Round to four decimal places as needed.) c. Are enjoying shopping for clothing and the gender of the individual statistically independent? Explain. O A. Yes, because P(malelenjoys shopping) = P(male). B. No, because P(male|enjoys shopping) = P(male). Oc. Yes, because P(malelenjoys shopping) + P(male). O D. No, because P(malelenjoys shopping) # P(male).
Chapter8: Sequences, Series,and Probability
Section8.7: Probability
Problem 11ECP: A manufacturer has determined that a machine averages one faulty unit for every 500 it produces....
Related questions
Question
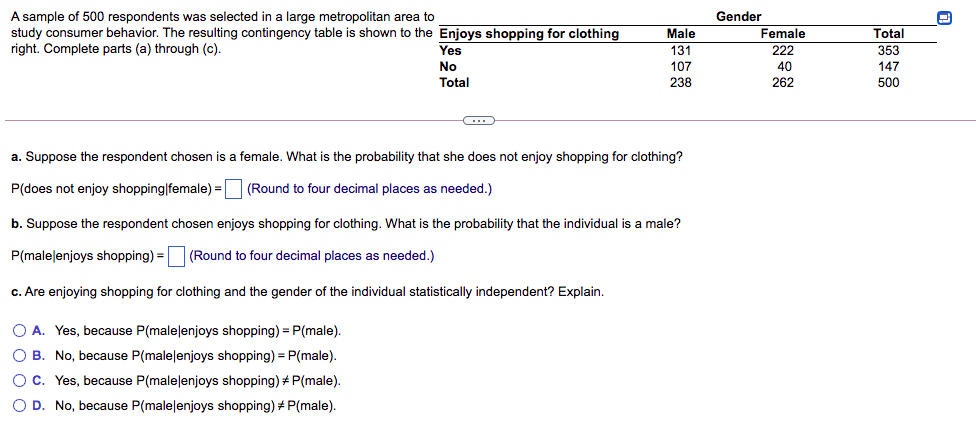
Transcribed Image Text:A sample of 500 respondents was selected in a large metropolitan area to
study consumer behavior. The resulting contingency table is shown to the Enjoys shopping for clothing
right. Complete parts (a) through (c).
Gender
Male
Female
Total
Yes
131
222
353
No
Total
107
40
147
238
262
500
a. Suppose the respondent chosen is a female. What is the probability that she does not enjoy shopping for clothing?
P(does not enjoy shopping|female) = (Round to four decimal places as needed.)
b. Suppose the respondent chosen enjoys shopping for clothing. What is the probability that the individual is a male?
P(malelenjoys shopping) =
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
c. Are enjoying shopping for clothing and the gender of the individual statistically independent? Explain.
O A. Yes, because P(malelenjoys shopping) = P(male).
O B. No, because P(malelenjoys shopping) =P(male).
O c. Yes, because P(malelenjoys shopping) + P(male).
O D. No, because P(malelenjoys shopping) + P(male).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

