A sample of difference scores from a repeated-measures experiment has a mean of Mp = 4 with a standard deviation of s = 6. If n = 9, is this sample sufficient to reject the null hypothesis using a two-tailed test with a = .05? t Distribution Degrees of Freedom = 19
A sample of difference scores from a repeated-measures experiment has a mean of Mp = 4 with a standard deviation of s = 6. If n = 9, is this sample sufficient to reject the null hypothesis using a two-tailed test with a = .05? t Distribution Degrees of Freedom = 19
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
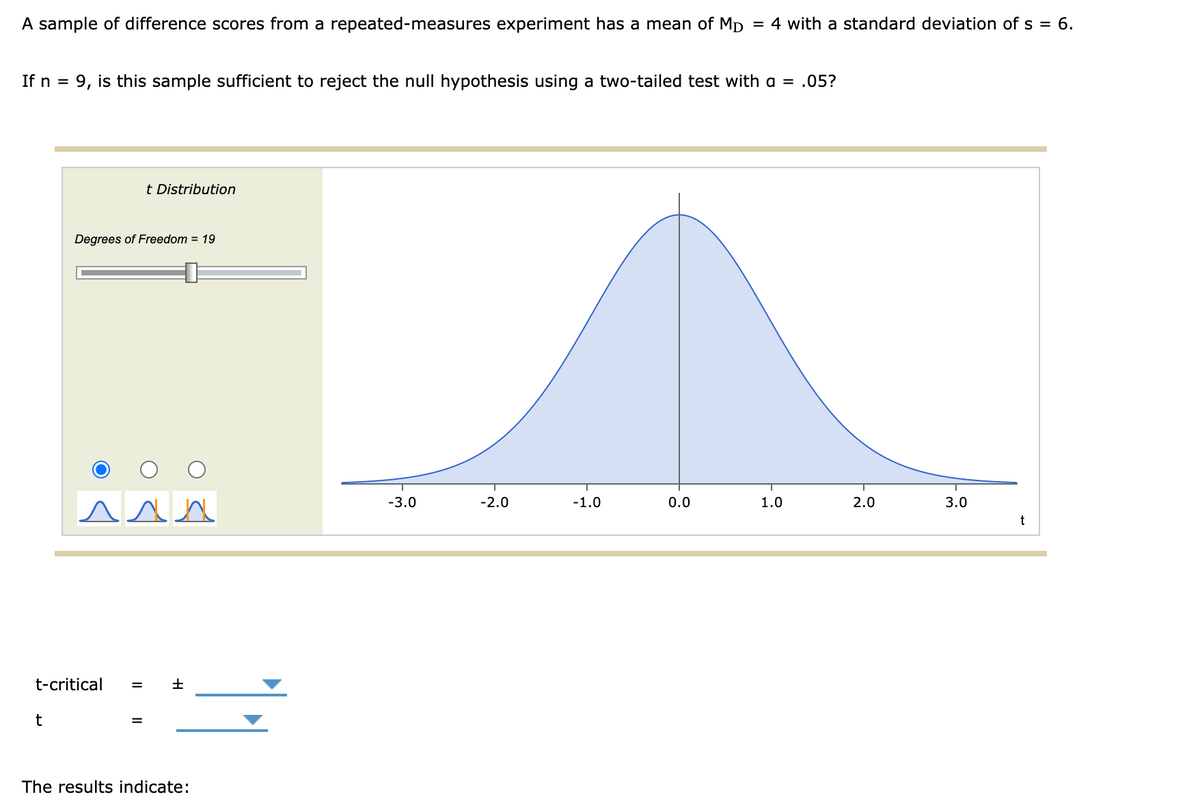
Transcribed Image Text:A sample of difference scores from a repeated-measures experiment has a mean of MD
4 with a standard deviation of s = 6.
If n =
9, is this sample sufficient to reject the null hypothesis using a two-tailed test with a = .05?
t Distribution
Degrees of Freedom = 19
A AA
-3.0
-2.0
-1.0
0.0
1.0
2.0
3.0
t
t-critical
t
The results indicate:

Transcribed Image Text:Failure to reject the null hypothesis; there is no significant mean difference
Failure to reject the null hypothesis; there is a significant mean difference
Rejection of the null hypothesis; there is no significant mean difference
Rejection of the null hypothesis; there is a significant mean difference
Would you reject Ho if n = 36? Again, assume a two-tailed test with a = .05.
t-critical
The results indicate:
Failure to reject the null hypothesis; there is a significant mean difference
Failure to reject the null hypothesis; there is no significant mean difference
Rejection of the null hypothesis; there is a significant mean difference
Rejection of the null hypothesis; there is no significant mean difference
Explain how the size of the sample influences the likelihood of finding a significant mean difference.
The sample size does not influence the likelihood of finding a significant mean difference.
The smaller the sample size, the greater the likelihood of finding a significant mean difference.
The larger the sample size, the greater the likelihood of finding a significant mean difference.
The larger the sample size, the smaller the likelihood of finding a significant mean difference.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman