A sample of hydrogen gas at a pressure of 1.14 atm and a temperature of 26.4° C, occupies a volume of 15.3 L. If the gas is allowed to expand at constant temperature to a volume of 20.3 L, the pressure of the gas sample will be atm.
A sample of hydrogen gas at a pressure of 1.14 atm and a temperature of 26.4° C, occupies a volume of 15.3 L. If the gas is allowed to expand at constant temperature to a volume of 20.3 L, the pressure of the gas sample will be atm.
Chapter6: The States Of Matter
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6.38E
Related questions
Question
100%
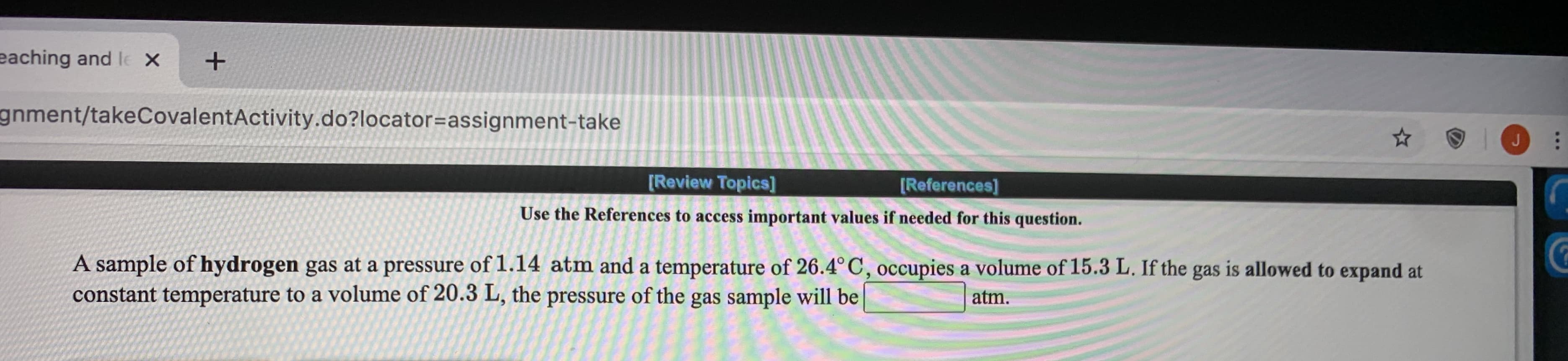
Transcribed Image Text:A sample of hydrogen gas at a pressure of 1.14 atm and a temperature of 26.4° C, occupies a volume of 15.3 L. If the gas is allowed to expand at
constant temperature to a volume of 20.3 L, the pressure of the gas sample will be
atm.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co


Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305960060
Author:
Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning