(a) Select all of the correct statements about reaction rates from the choices below. The lower the rate of a reaction the longer it takes to reach completion. Reaction rates decrease with increasing temperature. O Reaction rate constants increase with increasing temperature. A balanced chemical reaction is necessary to relate the rate of disappearance of a reactant to the rate of appearance of a product. O Reaction rates increase with increasing temperature. As a reaction progresses its rate goes down. Reaction rates are determined by reactant concentrations, temperatures, and reactant stabilities.
(a) Select all of the correct statements about reaction rates from the choices below. The lower the rate of a reaction the longer it takes to reach completion. Reaction rates decrease with increasing temperature. O Reaction rate constants increase with increasing temperature. A balanced chemical reaction is necessary to relate the rate of disappearance of a reactant to the rate of appearance of a product. O Reaction rates increase with increasing temperature. As a reaction progresses its rate goes down. Reaction rates are determined by reactant concentrations, temperatures, and reactant stabilities.
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Chapter8: Reaction Rates And Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8.20E: In each of the following, which reaction mechanism assumption is apparently being violated? Explain...
Related questions
Question
Give a clear explanation answer
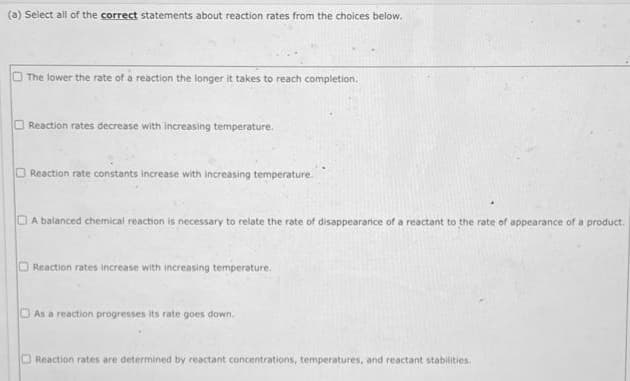
Transcribed Image Text:(a) Select all of the correct statements about reaction rates from the choices below.
U
The lower the rate of a reaction the longer it takes to reach completion.
Reaction rates decrease with increasing temperature.
Reaction rate constants increase with increasing temperature.
A balanced chemical reaction is necessary to relate the rate of disappearance of a reactant to the rate of appearance of a product.
Reaction rates increase with increasing temperature.
DAs a reaction progresses its rate goes down.
Reaction rates are determined by reactant concentrations, temperatures, and reactant stabilities.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305960060
Author:
Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305960060
Author:
Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781938168390
Author:
Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:
OpenStax