A simple random sample of front-seat occupants involved in car crashes is obtained. Among 2907 occupants not wearing seat belts, 39 were killed. Among 7772 occupants wearing seat belts, 17 were killed. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that seat belts are effective in reducing fatalities. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. Test the claim using a hypothesis test. Consider the first sample to be the sample of occupants not wearing seat belts and the second sample to be the sample of occupants wearing seat belts. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? O A. Ho: P1 = P2 H: P1 P2 O E. Ho: P1 = P2 H1: P1 * P2 OF. Ho: P1 * P2 H1: P1 = P2 Identify the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Identify the P-value. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What is the conclusion based on the hypothesis test? The Paralue ir Loronto than
A simple random sample of front-seat occupants involved in car crashes is obtained. Among 2907 occupants not wearing seat belts, 39 were killed. Among 7772 occupants wearing seat belts, 17 were killed. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that seat belts are effective in reducing fatalities. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. Test the claim using a hypothesis test. Consider the first sample to be the sample of occupants not wearing seat belts and the second sample to be the sample of occupants wearing seat belts. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? O A. Ho: P1 = P2 H: P1 P2 O E. Ho: P1 = P2 H1: P1 * P2 OF. Ho: P1 * P2 H1: P1 = P2 Identify the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Identify the P-value. P-value = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What is the conclusion based on the hypothesis test? The Paralue ir Loronto than
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
12th Edition
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Chapter8: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section8.7: Probability
Problem 6E: List the sample space of each experiment. Tossing three coins
Related questions
Question
Need help with these statistics questions
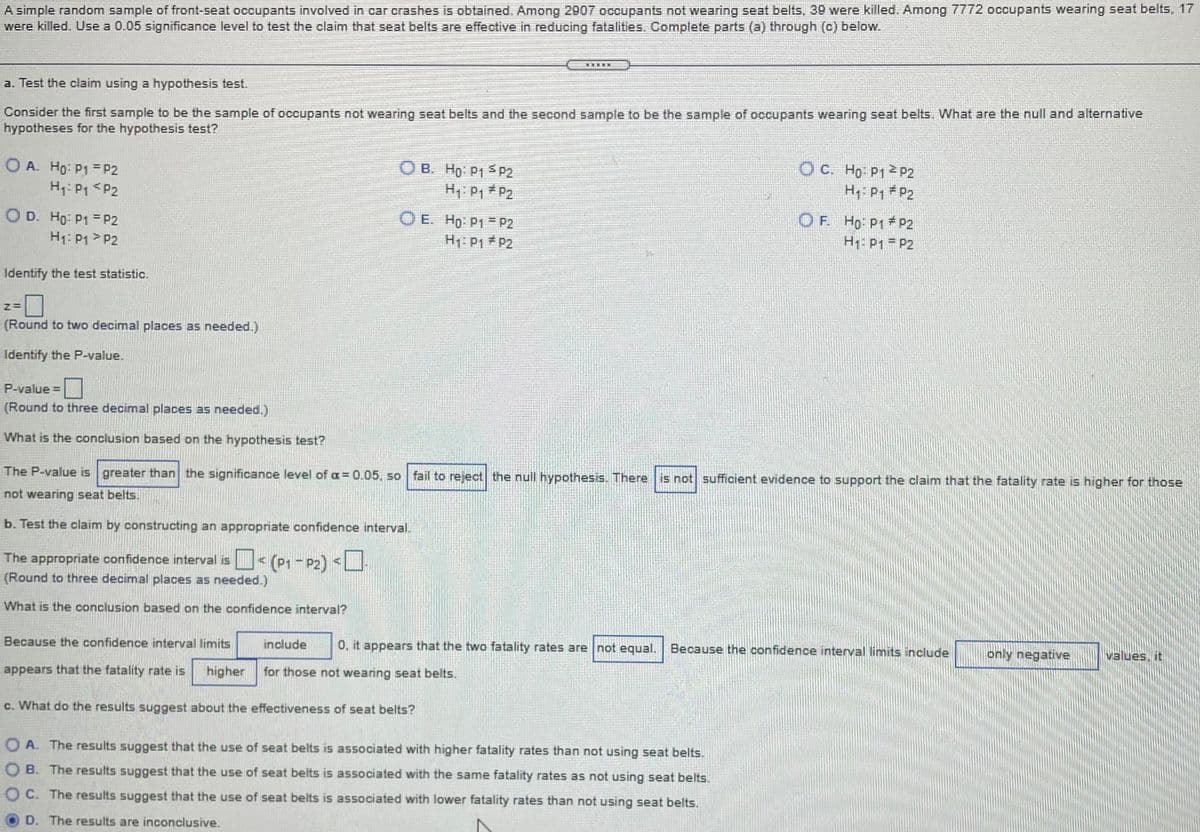
Transcribed Image Text:A simple random sample of front-seat occupants involved in car crashes is obtained. Among 2907 occupants not wearing seat belts, 39 were killed. Among 7772 occupants wearing seat belts, 17
were killed. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that seat belts are effective in reducing fatalities. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
a. Test the claim using a hypothesis test.
Consider the first sample to be the sample of occupants not wearing seat belts and the second sample to be the sample of occupants wearing seat belts. What are the null and alternative
hypotheses for the hypothesis test?
O A. Ho: P1 = P2
H1: P1 <P2
OB. Ho P1 P2
OC. Ho P12 P2
H: P1 # P2
H1: P1 # P2
O D. Ho: P1 = P2
H1: P1 > P2
O E. Ho: P1 = P2
H1: P1 P2
OF. Ho P1 P2
H1: P1 = P2
Identify the test statistic.
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Identify the P-value.
P-value =
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
What is the conclusion based on the hypothesis test?
The P-value is greater than the significance level of oa = 0.05, so fail to reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that the fatality rate is higher for those
not wearing seat belts.
b. Test the claim by constructing an appropriate confidence interval.
The appropriate confidence interval is< (P1 - P2) <
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
What is the conclusion based on the confidence interval?
Because the confidence interval limits
include
0, it appears that the two fatality rates are not equal.
Because the confidence interval limits include
only negative
values, it
appears that the fatality rate is
higher
for those not wearing seat belts.
c. What do the results suggest about the effectiveness of seat belts?
O A. The results suggest that the use of seat belts is associated with higher fatality rates than not using seat belts.
O B. The results suggest that the use of seat belts is associated with the same fatality rates as not using seat belts.
C. The results suggest that the use of seat belts is associated with lower fatality rates than not using seat belts.
D. The results are inconclusive.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning