A simple random sample of front-seat occupants involved in car crashes is obtained. Among 2957 occupants not wearing seat belts, 34 were killed. Among 7762 occupants wearing seat belts, 13 were killed. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that seat belts are effective in reducing fatalities. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. Test the claim using a hypothesis test. Consider the first sample to be the sample of occupants not wearing seat belts and the second sample to be the sample of occupants wearing seat belts. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? O B. Ho: P1 = P2 H1: P1 P2 Identify the test statistic. z= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Identify the P-value.
A simple random sample of front-seat occupants involved in car crashes is obtained. Among 2957 occupants not wearing seat belts, 34 were killed. Among 7762 occupants wearing seat belts, 13 were killed. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that seat belts are effective in reducing fatalities. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. Test the claim using a hypothesis test. Consider the first sample to be the sample of occupants not wearing seat belts and the second sample to be the sample of occupants wearing seat belts. What are the null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test? O B. Ho: P1 = P2 H1: P1 P2 Identify the test statistic. z= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Identify the P-value.
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
12th Edition
ISBN:9781305652231
Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Chapter8: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section8.7: Probability
Problem 6E: List the sample space of each experiment. Tossing three coins
Related questions
Concept explainers
Contingency Table
A contingency table can be defined as the visual representation of the relationship between two or more categorical variables that can be evaluated and registered. It is a categorical version of the scatterplot, which is used to investigate the linear relationship between two variables. A contingency table is indeed a type of frequency distribution table that displays two variables at the same time.
Binomial Distribution
Binomial is an algebraic expression of the sum or the difference of two terms. Before knowing about binomial distribution, we must know about the binomial theorem.
Topic Video
Question

Transcribed Image Text:A simple random sample of front-seat occupants involved in car crashes is obtained. Among 2957 occupants not wearing seat belts, 34 were killed. Among 7762
occupants wearing seat belts, 13 were killed. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that seat belts are effective in reducing fatalities. Complete parts (a) through
(c) below.
a. Test the claim using a hypothesis test.
Consider the first sample to be the sample of occupants not wearing seat belts and the second sample to be the sample of occupants wearing seat belts. What are the
null and alternative hypotheses for the hypothesis test?
О А. Но: Р1 2 P2
H1: P1 # P2
C. Ho: P1 + P2
H1:P1 = P2
B. Ho: P1 = P2
H1: P1 <P2
O D. Ho: P1 <P2
H1:P1 #P2
E. Ho: P1 = P2
H1:P1 # P2
F. Ho: P1 = P2
H1: P1 > P2
Identify the test statistic.
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Identify the P-value.
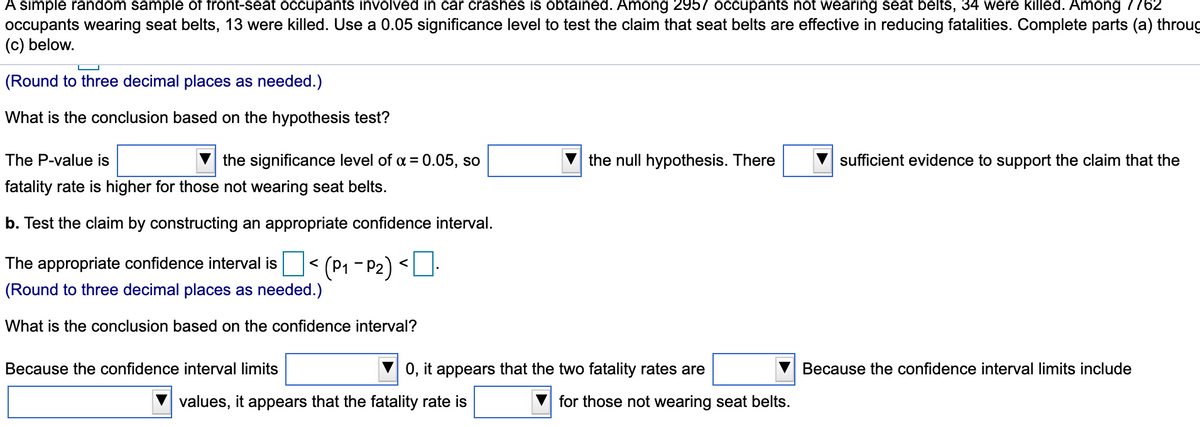
Transcribed Image Text:A simple random sample of front-seat occupants involved in car crashes is obtained. Among 2957 occupants not wearing seat belts, 34 were killed. Among 7762
occupants wearing seat belts, 13 were killed. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that seat belts are effective in reducing fatalities. Complete parts (a) throug
(c) below.
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
What is the conclusion based on the hypothesis test?
The P-value is
the significance level of a = 0.05, so
the null hypothesis. There
sufficient evidence to support the claim that the
fatality rate is higher for those not wearing seat belts.
b. Test the claim by constructing an appropriate confidence interval.
The appropriate confidence interval is
<
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
What is the conclusion based on the confidence interval?
Because the confidence interval limits
0, it appears that the two fatality rates are
Because the confidence interval limits include
values, it appears that the fatality rate is
for those not wearing seat belts.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
