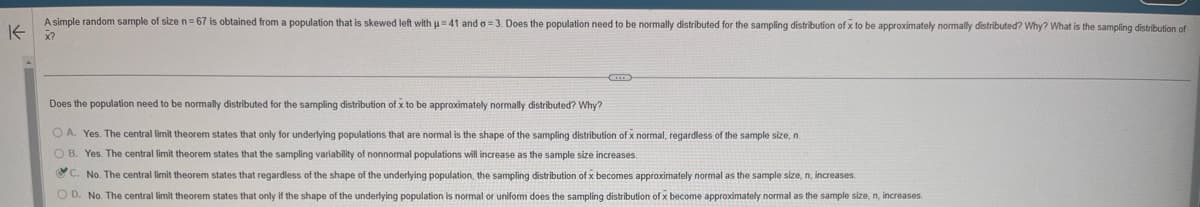
不 A simple random sample of size n=67 is obtained from a population that is skewed left with u 41 and a 3. Does the population need to be normally distributed for the sampling distribution of x to be approximately normally distributed? Why? What is the sampling distribution of m Does the population need to be normally distributed for the sampling distribution of x to be approximately normally distributed? Why? OA. Yes. The central limit theorem states that only for underlying populations that are normal is the shape of the sampling distribution of x normal, regardless of the sample size, n. OB. Yes. The central limit theorem states that the sampling variability of nonnormal populations will increase as the sample size increases. C. No. The central limit theorem states that regardless of the shape of the underlying population, the sampling distribution of x becomes approximately normal as the sample size, n, increases. OD. No. The central limit theorem states that only if the shape of the underlying population is normal or uniform does the sampling distribution of x become approximately normal as the sample size, n, increases.
不 A simple random sample of size n=67 is obtained from a population that is skewed left with u 41 and a 3. Does the population need to be normally distributed for the sampling distribution of x to be approximately normally distributed? Why? What is the sampling distribution of m Does the population need to be normally distributed for the sampling distribution of x to be approximately normally distributed? Why? OA. Yes. The central limit theorem states that only for underlying populations that are normal is the shape of the sampling distribution of x normal, regardless of the sample size, n. OB. Yes. The central limit theorem states that the sampling variability of nonnormal populations will increase as the sample size increases. C. No. The central limit theorem states that regardless of the shape of the underlying population, the sampling distribution of x becomes approximately normal as the sample size, n, increases. OD. No. The central limit theorem states that only if the shape of the underlying population is normal or uniform does the sampling distribution of x become approximately normal as the sample size, n, increases.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section10.8: Probability
Problem 10E
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:K
A simple random sample of size n = 67 is obtained from a population that is skewed left with u=41 and a 3. Does the population need to be normally distributed for the sampling distribution of x to be approximately normally distributed? Why? What is the sampling distribution of
X?
Does the population need to be normally distributed for the sampling distribution of x to be approximately normally distributed? Why?
A. Yes. The central limit theorem states that only for underlying populations that are normal is the shape of the sampling distribution of x normal, regardless of the sample size, n.
OB. Yes. The central limit theorem states that the sampling variability of nonnormal populations will increase as the sample size increases.
C. No. The central limit theorem states that regardless of the shape of the underlying population, the sampling distribution of x becomes approximately normal as the sample size, n, increases.
OD. No. The central limit theorem states that only if the shape of the underlying population is normal or uniform does the sampling distribution of x become approximately normal as the sample size, n, increases.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 12 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage