A soap manufacturer has the production function q = LK² and faces a wage rate of $45 and rental rate of capital of $90. (a) Find the cost-minimizing ratio of capital to labor. (This is also called the output expansion path). (b) Suppose the firm plans to produce q=1,000. Determine the cost- minimizing amount of labor and capital. (c) How much will it cost to produce q=1,000 (long run)? (d) Suppose the firm decides to increase its output to q = 1331, but is unable to increase its quantity of capital from the amount in b. How much labor will the firm need to employ and what will be the cost of producing q = 1331? (e) If the firm continues to produce q = 1331 over a long period of time, how will it alter its capital and labor from part d.? What will it cost to produce q = 1331 in the long run? On a graph, draw the two isoquants from above and the isocost lines corresponding to the LR and SR costs (there should be three). Identify the optimal L and K for each part on the graph. (f)
A soap manufacturer has the production function q = LK² and faces a wage rate of $45 and rental rate of capital of $90. (a) Find the cost-minimizing ratio of capital to labor. (This is also called the output expansion path). (b) Suppose the firm plans to produce q=1,000. Determine the cost- minimizing amount of labor and capital. (c) How much will it cost to produce q=1,000 (long run)? (d) Suppose the firm decides to increase its output to q = 1331, but is unable to increase its quantity of capital from the amount in b. How much labor will the firm need to employ and what will be the cost of producing q = 1331? (e) If the firm continues to produce q = 1331 over a long period of time, how will it alter its capital and labor from part d.? What will it cost to produce q = 1331 in the long run? On a graph, draw the two isoquants from above and the isocost lines corresponding to the LR and SR costs (there should be three). Identify the optimal L and K for each part on the graph. (f)
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
5th Edition
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Chapter4: Extent (how Much) Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3MC
Related questions
Question
Please answer part d,e and f
and here is the answer of first three parts:
part c answer is 1350

Transcribed Image Text:Problem 1
LK² and faces a wage
A soap manufacturer has the production function q =
rate of $45 and rental rate of capital of $90.
(a)
Find the cost-minimizing ratio of capital to labor. (This is also
called the output expansion path).
(b)
Suppose the firm plans to produce q=1,000. Determine the cost-
minimizing amount of labor and capital.
(c)
How much will it cost to produce q=1,000 (long run)?
Suppose the firm decides to increase its output to q = 1331, but is
unable to increase its quantity of capital from the amount in b. How
much labor will the firm need to employ and what will be the cost
of producing q = 1331?
(d)
(e)
If the firm continues to produce q = 1331 over a long period of time,
how will it alter its capital and labor from part d.? What will it cost
to produce q = 1331 in the long run?
On a graph, draw the two isoquants from above and the isocost
lines corresponding to the LR and SR costs (there should be three).
Identify the optimal L and K for each part on the graph.
(f)
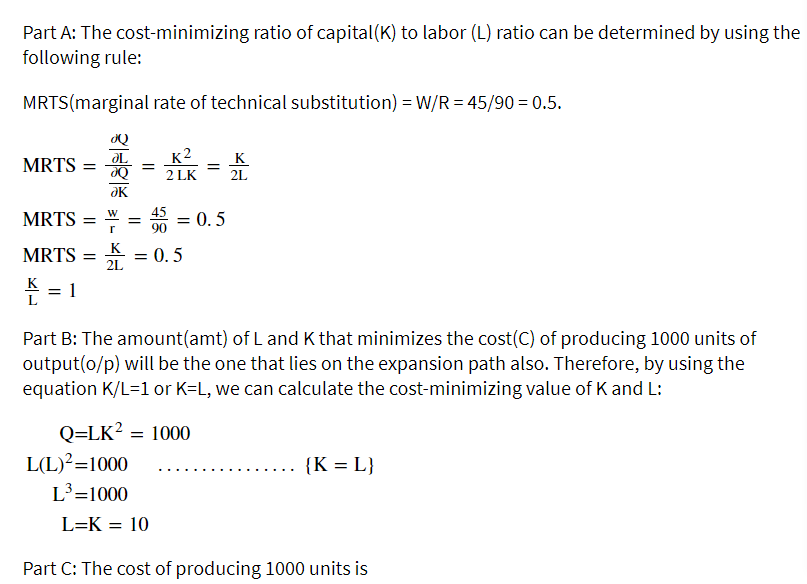
Transcribed Image Text:Part A: The cost-minimizing ratio of capital(K) to labor (L) ratio can be determined by using the
following rule:
MRTS(marginal rate of technical substitution) = W/R = 45/90 = 0.5.
OL
MRTS =
_K2
2 LK
K
2L
MRTS
= 0. 5
K
MRTS
= 0. 5
2L
K
= 1
L
Part B: The amount(amt) of L and K that minimizes the cost(C) of producing 1000 units of
output(o/p) will be the one that lies on the expansion path also. Therefore, by using the
equation K/L=1 or K=L, we can calculate the cost-minimizing value of K and L:
Q=LK? = 1000
L(L)?=1000
{K = L}
L³=1000
L=K = 10
Part C: The cost of producing 1000 units is
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Microeconomics: Principles & Policy
Economics
ISBN:
9781337794992
Author:
William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. Solow
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
