A solid piece of lead has a mass of 29.89 g and a volume of 2.67 cm³. From these data, calculate the density of lead in SI units (kilograms per cubic meter). Step 1 The density of lead is 1.13 × 10ª kg/m³, so we should expect our calculated value to be close to this value. The density of water is 1.00 x 10³ kg/m3, so we see that lead is about 11 times denser than water, which agrees with our experience that lead sinks. Step 2 Density is defined as p = m/V. We must convert to SI units in the calculation. Step 3 29.89 1 kg 11.1947 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. cm cm3 1000 g 2.67 1 m 11.1947 v cm3 1 kg 1000 g Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. g 1000000 1 1 m3 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. cm3 11190 Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. x 104 kg/m³
A solid piece of lead has a mass of 29.89 g and a volume of 2.67 cm³. From these data, calculate the density of lead in SI units (kilograms per cubic meter). Step 1 The density of lead is 1.13 × 10ª kg/m³, so we should expect our calculated value to be close to this value. The density of water is 1.00 x 10³ kg/m3, so we see that lead is about 11 times denser than water, which agrees with our experience that lead sinks. Step 2 Density is defined as p = m/V. We must convert to SI units in the calculation. Step 3 29.89 1 kg 11.1947 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. cm cm3 1000 g 2.67 1 m 11.1947 v cm3 1 kg 1000 g Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. g 1000000 1 1 m3 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. cm3 11190 Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. x 104 kg/m³
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter1: Introduction And Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 15P: Assume it takes 7.00 min to fill a 30.0-gal gasoline tank. (a) Calculate the rate at which the tank...
Related questions
Question
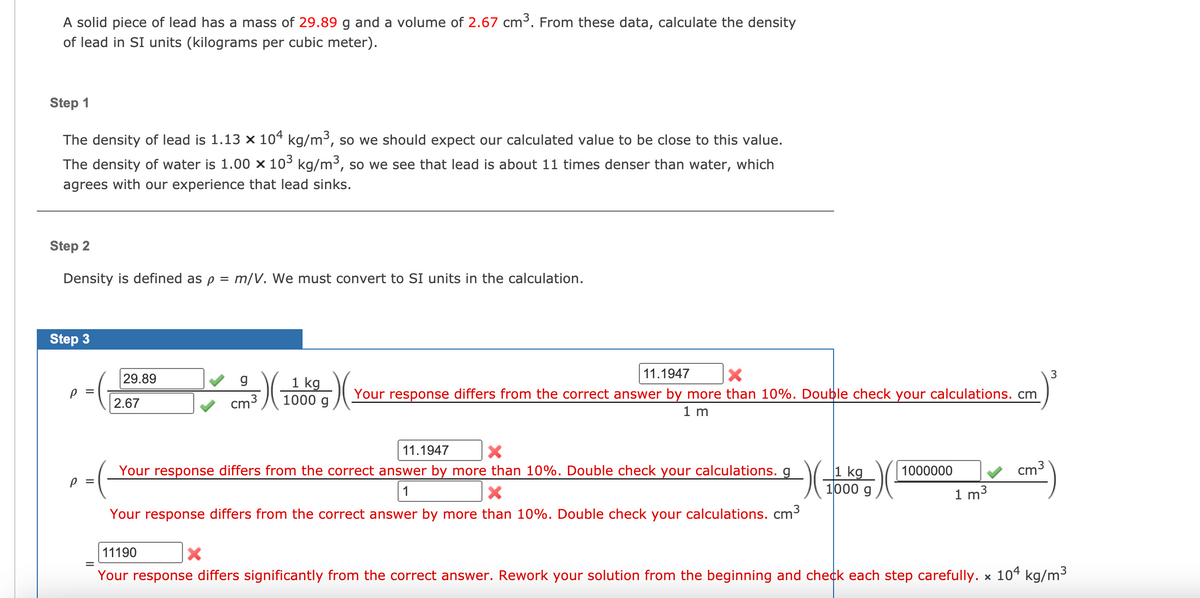
Transcribed Image Text:A solid piece of lead has a mass of 29.89 g and a volume of 2.67 cm³. From these data, calculate the density
of lead in SI units (kilograms per cubic meter).
Step 1
The density of lead is 1.13 x 104 kg/m³, so we should expect our calculated value to be close to this value.
The density of water is 1.00 × 103 kg/m3, so we see that lead is about 11 times denser than water, which
agrees with our experience that lead sinks.
Step 2
Density is defined as p = m/V. We must convert to SI units in the calculation.
Step 3
11.1947
29.89
1 kg
1000 g
Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. cm
2.67
cm3
1 m
11.1947
Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. g
cm3
1 kg
1000
1000000
P =
1
1 m3
Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. cm3
11190
Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. x 104 kg/m3
Expert Solution
Step 1
Given data:
Mass of solid piece (m) = 29.89 g
Volume (v) = 2.67 cm3
Need to determine the density of the block in SI unit.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:
9781305079137
Author:
James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning