A spring (k = 75 N/m) has an equilibrium length of 1.00 meter. The spring is compressed to a length of 0.50 m and a mass of 2.0 kg is placed at its free end on a frictionless slope which makes an angle of 41° with respect to the horizontal. The spring is then released. 0.50 m e = 41° (a) If the mass is not attached to the spring, how far up the slope will the mass move before coming to rest? (b) If the mass is attached to the spring, how far up the slope will the mass move before coming to rest? (c) Now the incline has a coefficient of kinetic friction uk. If the block, attached to the spring, is observed to stop as it reaches the spring's equilibrium position, what is µk?
A spring (k = 75 N/m) has an equilibrium length of 1.00 meter. The spring is compressed to a length of 0.50 m and a mass of 2.0 kg is placed at its free end on a frictionless slope which makes an angle of 41° with respect to the horizontal. The spring is then released. 0.50 m e = 41° (a) If the mass is not attached to the spring, how far up the slope will the mass move before coming to rest? (b) If the mass is attached to the spring, how far up the slope will the mass move before coming to rest? (c) Now the incline has a coefficient of kinetic friction uk. If the block, attached to the spring, is observed to stop as it reaches the spring's equilibrium position, what is µk?
College Physics
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter13: Vibrations And Waves
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 32P: A spring of negligible mass stretches 3.00 cm from its relaxed length when a force of 7.50 N is...
Related questions
Question
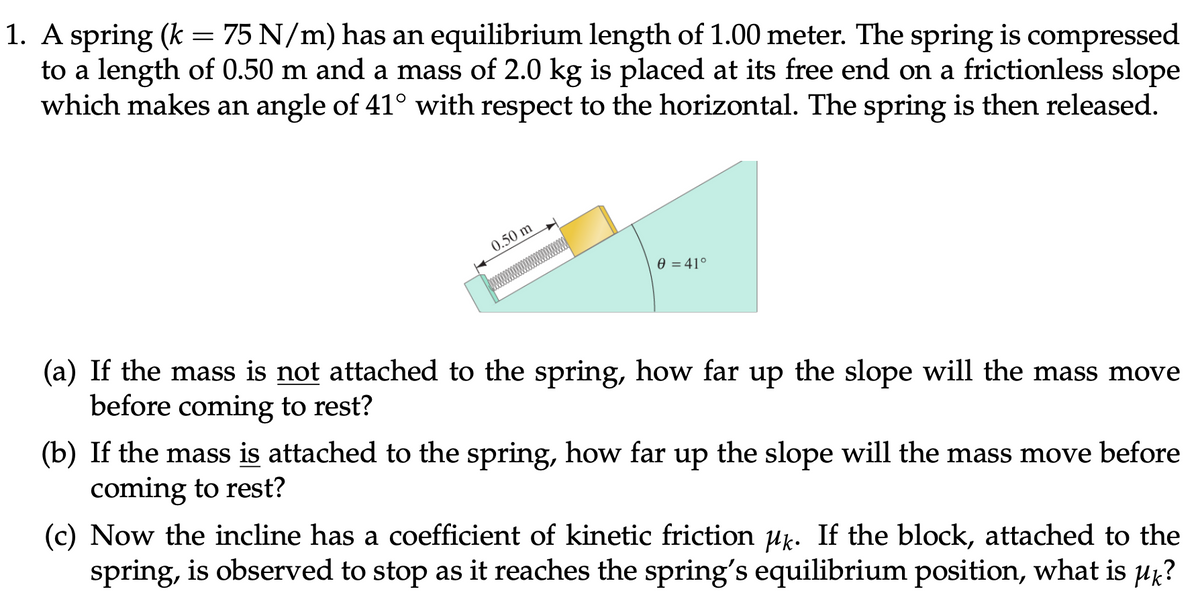
Transcribed Image Text:1. A spring (k = 75 N/m) has an equilibrium length of 1.00 meter. The spring is compressed
to a length of 0.50 m and a mass of 2.0 kg is placed at its free end on a frictionless slope
which makes an angle of 41° with respect to the horizontal. The spring is then released.
0.50 m
0 = 41°
(a) If the mass is not attached to the spring, how far up the slope will the mass move
before coming to rest?
(b) If the mass is attached to the spring, how far up the slope will the mass move before
coming to rest?
(c) Now the incline has a coefficient of kinetic friction uk. If the block, attached to the
spring, is observed to stop as it reaches the spring's equilibrium position, what is µk?
Expert Solution
Step 1
at highest point the spring energy will be converted into potential energy hence
so the distance up the slope
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning