A T www.royalonlineschool.ca/mod/assign/view.php?id%3D1180 Case: You are the CEO of Canadian Demolition which specializes in deconstruction of commercial buildings. In this process, your task is to demolish the building, preserve any valuable elements for reuse and dispose of the remaining materials as required by Canadian laws and regulations. In Canada, any hazardous materials (such as lead paint, mercury switches, hazardous chemicals, etc.) must be identified, documented, collected and disposed of following strict processes and regulations. Although a very costly process, all licensed demolition companies must follow these regulations or risk losing their accreditation with Canada Environmental Health and Safety. For all other materials, the business is able to simply dispose of them at a local dump or landfill.
A T www.royalonlineschool.ca/mod/assign/view.php?id%3D1180 Case: You are the CEO of Canadian Demolition which specializes in deconstruction of commercial buildings. In this process, your task is to demolish the building, preserve any valuable elements for reuse and dispose of the remaining materials as required by Canadian laws and regulations. In Canada, any hazardous materials (such as lead paint, mercury switches, hazardous chemicals, etc.) must be identified, documented, collected and disposed of following strict processes and regulations. Although a very costly process, all licensed demolition companies must follow these regulations or risk losing their accreditation with Canada Environmental Health and Safety. For all other materials, the business is able to simply dispose of them at a local dump or landfill.
Chapter1: Taking Risks And Making Profits Within The Dynamic Business Environment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1CE
Related questions
Question
do only (A) part, please
Transcribed Image Text:A TE www.royalonlineschool.ca/mod/assign/view.php?id%3D1180
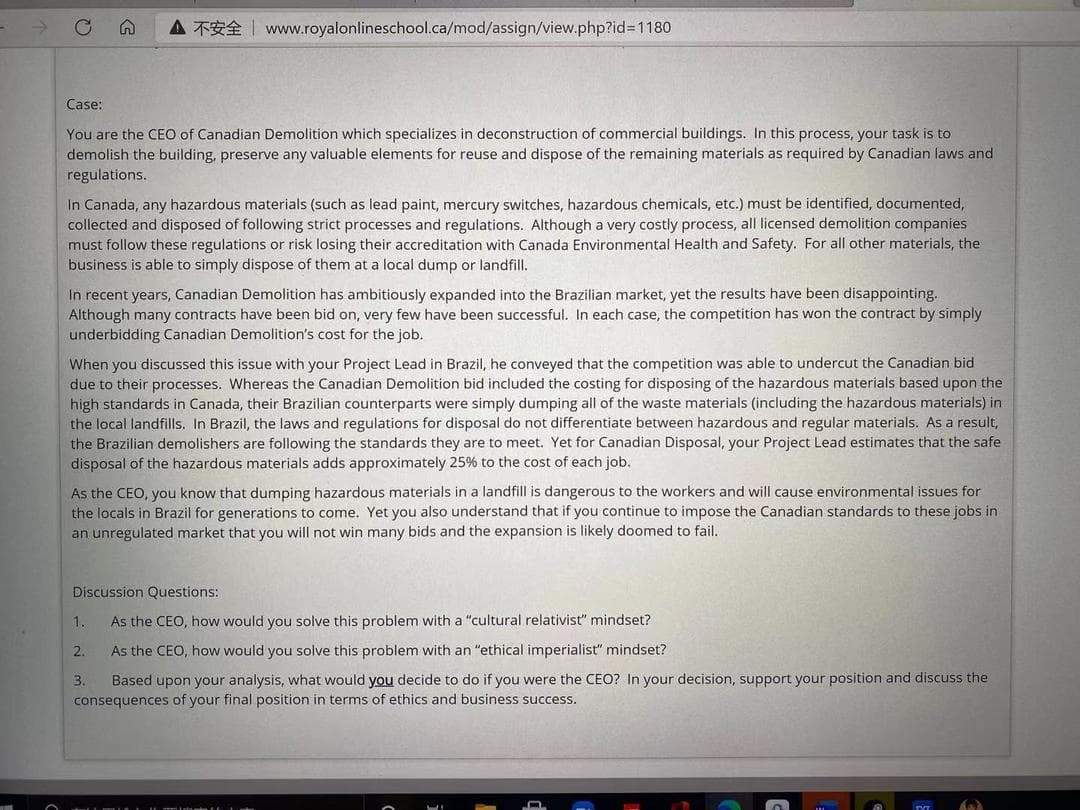
Case:
You are the CEO of Canadian Demolition which specializes in deconstruction of commercial buildings. In this process, your task is to
demolish the building, preserve any valuable elements for reuse and dispose of the remaining materials as required by Canadian laws and
regulations.
In Canada, any hazardous materials (such as lead paint, mercury switches, hazardous chemicals, etc.) must be identified, documented,
collected and disposed of following strict processes and regulations. Although a very costly process, all licensed demolition companies
must follow these regulations or risk losing their accreditation with Canada Environmental Health and Safety. For all other materials, the
business is able to simply dispose of them at a local dump or landfill.
In recent years, Canadian Demolition has ambitiously expanded into the Brazilian market, yet the results have been disappointing.
Although many contracts have been bid on, very few have been successful. In each case, the competition has won the contract by simply
underbidding Canadian Demolition's cost for the job.
When you discussed this issue with your Project Lead in Brazil, he conveyed that the competition was able to undercut the Canadian bid
due to their processes. Whereas the Canadian Demolition bid included the costing for disposing of the hazardous materials based upon the
high standards in Canada, their Brazilian counterparts were simply dumping all of the waste materials (including the hazardous materials) in
the local landfills. In Brazil, the laws and regulations for disposal do not differentiate between hazardous and regular materials. As a result,
the Brazilian demolishers are following the standards they are to meet. Yet for Canadian Disposal, your Project Lead estimates that the safe
disposal of the hazardous materials adds approximately 25% to the cost of each job.
As the CEO, you know that dumping hazardous materials in a landfill is dangerous to the workers and will cause environmental issues for
the locals in Brazil for generations to come. Yet you also understand that if you continue to impose the Canadian standards to these jobs in
an unregulated market that you will not win many bids and the expansion is likely doomed to fail.
Discussion Questions:
1.
As the CEO, how would you solve this problem with a "cultural relativist" mindset?
2.
As the CEO, how would you solve this problem with an "ethical imperialist" mindset?
Based upon your analysis, what would you decide to do if you were the CEO? In your decision, support your position and discuss the
consequences of your final position in terms of ethics and business success.
3.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, management and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Understanding Business
Management
ISBN:
9781259929434
Author:
William Nickels
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Management (14th Edition)
Management
ISBN:
9780134527604
Author:
Stephen P. Robbins, Mary A. Coulter
Publisher:
PEARSON

Spreadsheet Modeling & Decision Analysis: A Pract…
Management
ISBN:
9781305947412
Author:
Cliff Ragsdale
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Understanding Business
Management
ISBN:
9781259929434
Author:
William Nickels
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Management (14th Edition)
Management
ISBN:
9780134527604
Author:
Stephen P. Robbins, Mary A. Coulter
Publisher:
PEARSON

Spreadsheet Modeling & Decision Analysis: A Pract…
Management
ISBN:
9781305947412
Author:
Cliff Ragsdale
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Management Information Systems: Managing The Digi…
Management
ISBN:
9780135191798
Author:
Kenneth C. Laudon, Jane P. Laudon
Publisher:
PEARSON

Business Essentials (12th Edition) (What's New in…
Management
ISBN:
9780134728391
Author:
Ronald J. Ebert, Ricky W. Griffin
Publisher:
PEARSON

Fundamentals of Management (10th Edition)
Management
ISBN:
9780134237473
Author:
Stephen P. Robbins, Mary A. Coulter, David A. De Cenzo
Publisher:
PEARSON