A tennis ball is thrown upward at an angle from point A. It follows a parabolic trajectory and hits the ground at point D. At the instant shown, the ball is at point B. Point C represents the highest position of the ball above the ground. B INGE While in flight, how do the x and y components of the velocity vector of the ball compare at the points A and D? A The velocity components are non-zero at A and are zero m/s at D. The velocity components have the same magnitudes at both points, but the directions of the x B components are reversed. The velocity components have the same magnitudes at both points, but their directions are reversed. The velocity components have the same magnitudes at both points, but the directions of the y D) components are reversed.
A tennis ball is thrown upward at an angle from point A. It follows a parabolic trajectory and hits the ground at point D. At the instant shown, the ball is at point B. Point C represents the highest position of the ball above the ground. B INGE While in flight, how do the x and y components of the velocity vector of the ball compare at the points A and D? A The velocity components are non-zero at A and are zero m/s at D. The velocity components have the same magnitudes at both points, but the directions of the x B components are reversed. The velocity components have the same magnitudes at both points, but their directions are reversed. The velocity components have the same magnitudes at both points, but the directions of the y D) components are reversed.
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter2: Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 44P: A chameleon is resting quietly on a lanai screen, waiting for an insect to come by. Assume the...
Related questions
Question
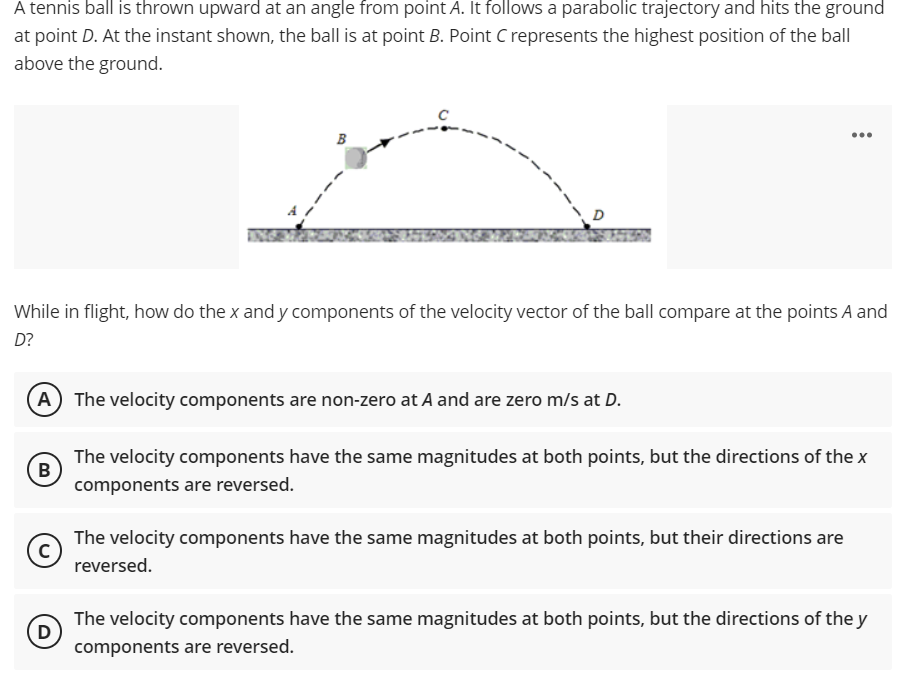
Transcribed Image Text:A tennis ball is thrown upward at an angle from point A. It follows a parabolic trajectory and hits the ground
at point D. At the instant shown, the ball is at point B. Point C represents the highest position of the ball
above the ground.
...
B
D
INGE
While in flight, how do the x and y components of the velocity vector of the ball compare at the points A and
D?
A The velocity components are non-zero at A and are zero m/s at D.
The velocity components have the same magnitudes at both points, but the directions of the x
B
components are reversed.
The velocity components have the same magnitudes at both points, but their directions are
reversed.
D
The velocity components have the same magnitudes at both points, but the directions of the y
components are reversed.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill