A toy submarine of mass m = 0.830 kg moves around a submerged circular track of radius R = 1.97 m. The submarine's engine provides a constant propulsion force of F = 4.93 N. When the sub is in motion, it is subject to a viscous drag force exerted by the water. This force is proportional to the sub's speed; the proportionality factor is C = 1.26 kg/s. Assuming it starts from rest at t = O s, the speed v (t) of the submarine at a later time t is given by F v() = (1 - e-Cilm) where e is the base of the natural logarithm. How much time has passed when the submarine's speed reaches 59% of its terminal value? What is the magnitude of the submarine's acceleration a at this time?
A toy submarine of mass m = 0.830 kg moves around a submerged circular track of radius R = 1.97 m. The submarine's engine provides a constant propulsion force of F = 4.93 N. When the sub is in motion, it is subject to a viscous drag force exerted by the water. This force is proportional to the sub's speed; the proportionality factor is C = 1.26 kg/s. Assuming it starts from rest at t = O s, the speed v (t) of the submarine at a later time t is given by F v() = (1 - e-Cilm) where e is the base of the natural logarithm. How much time has passed when the submarine's speed reaches 59% of its terminal value? What is the magnitude of the submarine's acceleration a at this time?
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter5: More Applications Of Newton’s Laws
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 49P: A space station, in the form of a wheel 120 m in diameter, rotates to provide an artificial gravity...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
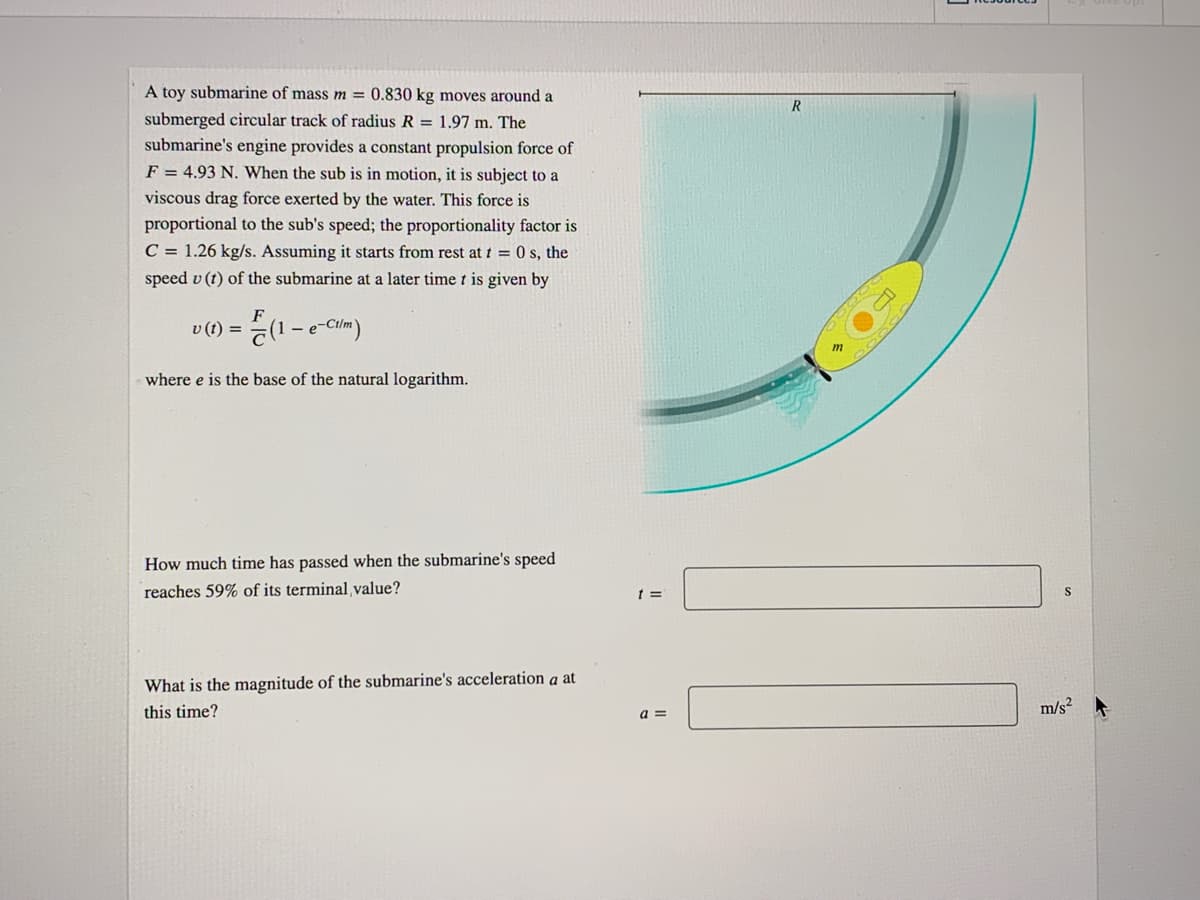
Transcribed Image Text:A toy submarine of mass m = 0.830 kg moves around a
submerged circular track of radius R = 1.97 m. The
submarine's engine provides a constant propulsion force of
F = 4.93 N. When the sub is in motion, it is subject to a
viscous drag force exerted by the water. This force is
proportional to the sub's speed; the proportionality factor is
C = 1.26 kg/s. Assuming it starts from rest at t = 0 s, the
speed v (t) of the submarine at a later time t is given by
v (1) = (1 - e-Cim)
%3D
where e is the base of the natural logarithm.
How much time has passed when the submarine's speed
reaches 59% of its terminal value?
t =
S
What is the magnitude of the submarine's acceleration a at
this time?
m/s?
a =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning