A variable of a population has a mean of u = 75 and a standard deviation of o = 16. a. Identify the sampling distribution of the sample mean for samples of size 64. b. In answering part (a), what assumptions did you make about the distribution of the variable? c. Can you answer part (a) if the sample size is 25 instead of 64? Why or why not? a. What is the shape of the sampling distribution? bimodal normal skewed O uniform What is the mean of the sampling distribution? H: = 60 (Simplify your answer.) What is the standard deviation of the sampling distribution? o: = 1.1 (Simplify your answer.)
A variable of a population has a mean of u = 75 and a standard deviation of o = 16. a. Identify the sampling distribution of the sample mean for samples of size 64. b. In answering part (a), what assumptions did you make about the distribution of the variable? c. Can you answer part (a) if the sample size is 25 instead of 64? Why or why not? a. What is the shape of the sampling distribution? bimodal normal skewed O uniform What is the mean of the sampling distribution? H: = 60 (Simplify your answer.) What is the standard deviation of the sampling distribution? o: = 1.1 (Simplify your answer.)
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.4: Distributions Of Data
Problem 19PFA
Related questions
Question
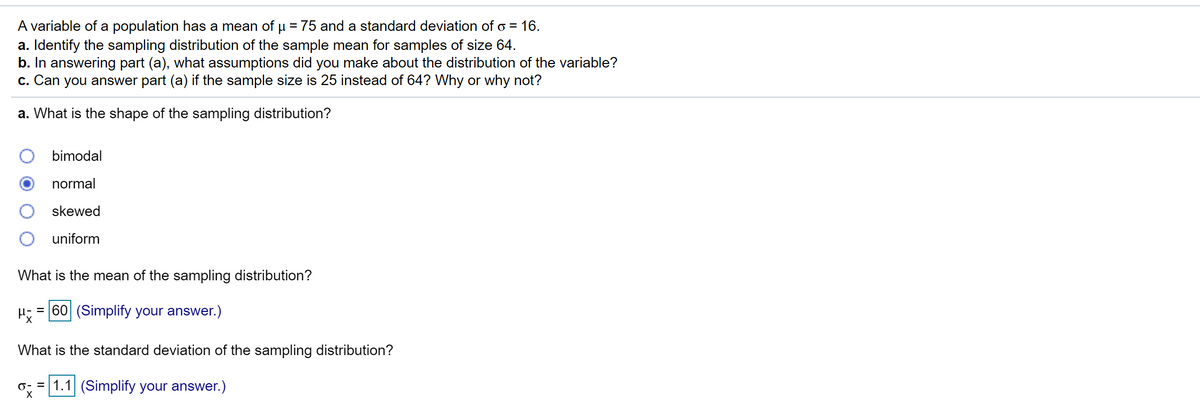
Transcribed Image Text:A variable of a population has a mean of µ = 75 and a standard deviation of o = 16.
a. Identify the sampling distribution of the sample mean for samples of size 64.
b. In answering part (a), what assumptions did you make about the distribution of the variable?
c. Can you answer part (a) if the sample size is 25 instead of 64? Why or why not?
a. What is the shape of the sampling distribution?
bimodal
normal
skewed
uniform
What is the mean of the sampling distribution?
= 60 (Simplify your answer.)
What is the standard deviation of the sampling distribution?
o; = 1.1 (Simplify your answer.)

Transcribed Image Text:b. In answering part (a), what assumptions did you make about the distribution of the variable?
A. It was assumed that the distribution of the variable was unimodal.
B. No assumptions were made because, for a relatively large sample size, the sampling distribution is normal, regardless of the distribution of the variable under consideration.
C. No assumptions were made because the sampling distribution is normal, regardless of the distribution of the variable under consideration.
D. It was assumed that the variable was normally distributed.
c. Can you answer part (a) if the sample size is 25 instead of 64? Why or why not?
O A. No, because the sample size needs to be at least 30 if the distribution of the variable is unknown.
B. No, because the sample size must be less than 5 if the distribution of the variable is unknown.
C. Yes, because the sample size must be less than 30 if the distribution of the variable is unknown.
D. Yes, because the sample size makes no difference in determining the sampling distribution.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill