(a) What are the null and alternate hypotheses? 0.001 0.010 (b) Suppose the P-value is approximately 0.0048, conclude the test using a (a=0.01) 1% level of significance. Does the test indicate that we should reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Explain.
(a) What are the null and alternate hypotheses? 0.001 0.010 (b) Suppose the P-value is approximately 0.0048, conclude the test using a (a=0.01) 1% level of significance. Does the test indicate that we should reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Explain.
Chapter8: Sequences, Series,and Probability
Section8.6: Counting Principles
Problem 74E: Lottery Powerball is a lottery game that is operated by the Multi-State Lottery Association and is...
Related questions
Question
100%
BADLY NEED SOLUTIONS FOR THIS!
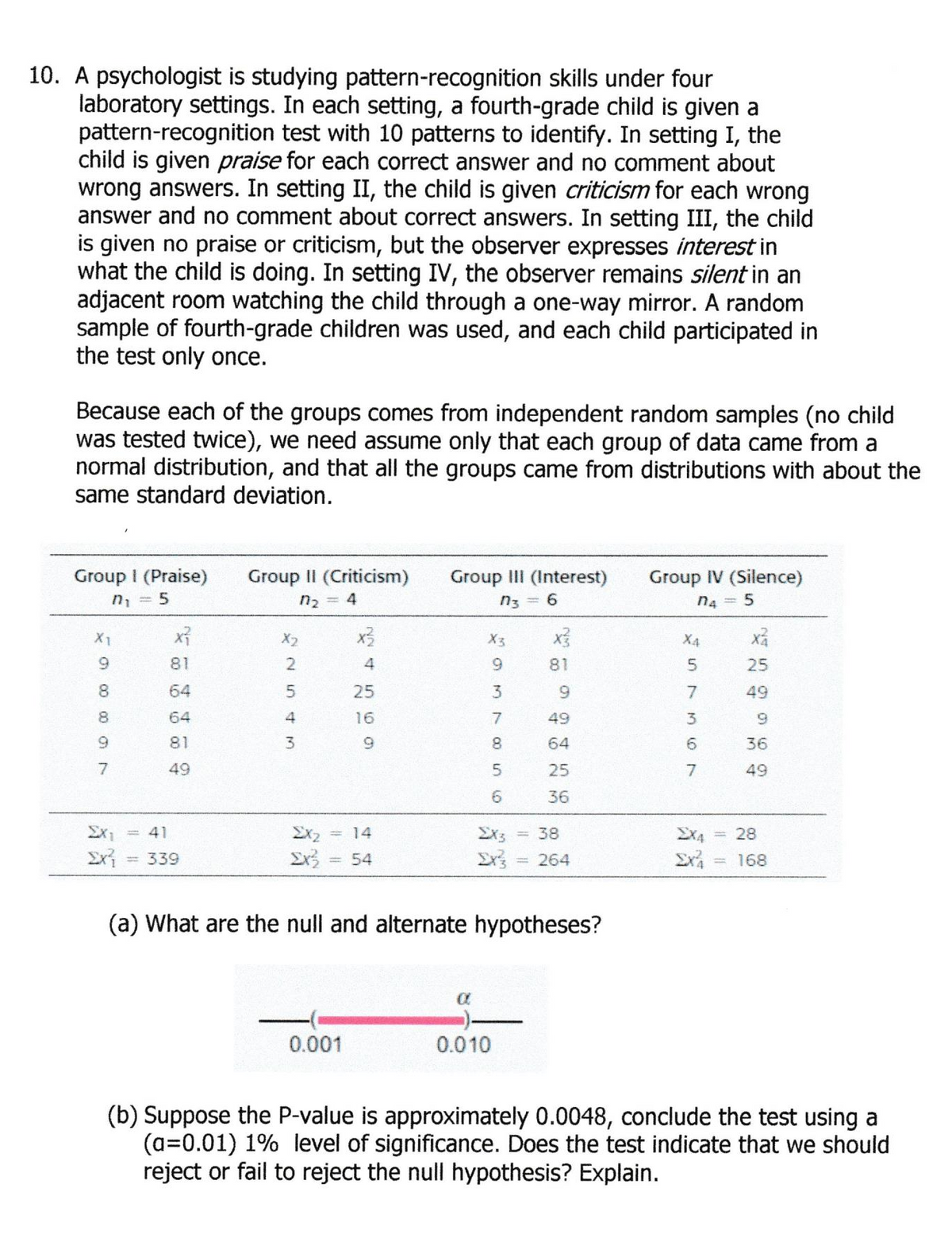
Transcribed Image Text:10. A psychologist is studying pattern-recognition skills under four
laboratory settings. In each setting, a fourth-grade child is given a
pattern-recognition test with 10 patterns to identify. In setting I, the
child is given praise for each correct answer and no comment about
wrong answers. In setting II, the child is given criticism for each wrong
answer and no comment about correct answers. In setting III, the child
is given no praise or criticism, but the observer expresses interest in
what the child is doing. In setting IV, the observer remains silent in an
adjacent room watching the child through a one-way mirror. A random
sample of fourth-grade children was used, and each child participated in
the test only once.
Because each of the groups comes from independent random samples (no child
was tested twice), we need assume only that each group of data came from a
normal distribution, and that all the groups came from distributions with about the
same standard deviation.
Group I (Praise)
Group II (Criticism)
Group III (Interest)
Group IV (Silence)
n, = 5
n2 = 4
n3 = 6
n4 = 5
X1
X2
x3
X3
X4
6.
81
4
9.
81
25
8
64
25
6.
7
49
8
64
16
49
9.
6.
81
9.
8.
64
6.
36
49
25
7.
49
6.
36
Ex1
= 41
Ex2
= 14
Ex3
= 38
EX4
28
339
54
= 264
= 168
(a) What are the null and alternate hypotheses?
0.001
0.010
(b) Suppose the P-value is approximately 0.0048, conclude the test using a
(a=0.01) 1% level of significance. Does the test indicate that we should
reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Explain.
1254 3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you


Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning