(a) What sample size should be obtained if he wants to be within 4 percentage points with 94% confidence if he uses an estimate of 52% obtained from a poll? The sample size is (Round up to the nearest integer.) (b) What sample size should be obtained if he wants to be within 4 percentage points with 94% confidence if he does not use any prior estimates? The sample size is. (Round up to the nearest integer.) (c) Why are the results from parts (a) and (b) so close? O A. The results are close because the confidence 94% is close to 100%. B. The results are close because the margin of error 4% is less than 5% OC. The results are close because 0.52(1-0.52) = 0.2496 is very close to 0.25.
(a) What sample size should be obtained if he wants to be within 4 percentage points with 94% confidence if he uses an estimate of 52% obtained from a poll? The sample size is (Round up to the nearest integer.) (b) What sample size should be obtained if he wants to be within 4 percentage points with 94% confidence if he does not use any prior estimates? The sample size is. (Round up to the nearest integer.) (c) Why are the results from parts (a) and (b) so close? O A. The results are close because the confidence 94% is close to 100%. B. The results are close because the margin of error 4% is less than 5% OC. The results are close because 0.52(1-0.52) = 0.2496 is very close to 0.25.
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.4: Distributions Of Data
Problem 19PFA
Related questions
Question
100%
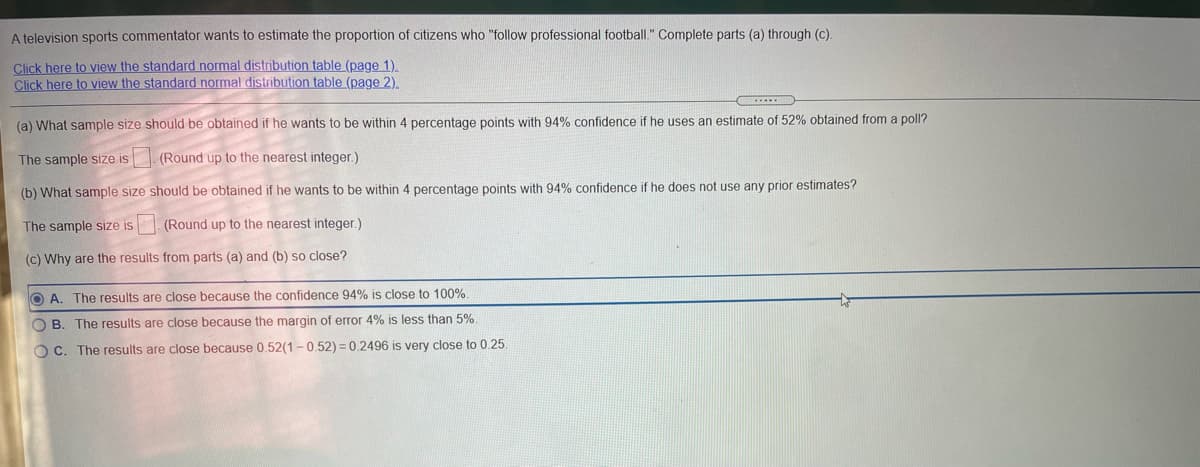
Transcribed Image Text:A television sports commentator wants to estimate the proportion of citizens who "follow professional football." Complete parts (a) through (c).
Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1).
Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2).
(a) What sample size should be obtained if he wants to be within 4 percentage points with 94% confidence if he uses an estimate of 52% obtained from a poll?
The sample size is (Round up to the nearest integer.)
(b) What sample size should be obtained if he wants to be within 4 percentage points with 94% confidence if he does not use any prior estimates?
The sample size is
(Round up to the nearest integer.)
(c) Why are the results from parts (a) and (b) so close?
O A. The results are close because the confidence 94% is close to 100%.
O B. The results are close because the margin of error 4% is less than 5%.
OC. The results are close because 0.52(1 -0.52) = 0.2496 is very close to 0.25.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill