a) Which of the three policies below do you think would be most effective? Policy 1: Increments drive a contractionary financial approach in the different base loan costs constrained by current national banks or different methods creating development in cash flexibly. The objective is to lessen swelling by restricting the measure of dynamic cash coursing in the economy. In this when the government reduce the rate of interest then the supply of money will be reduced in the economy and contraction monetary policy will be used by the government to control the money because the reserve repo rate will be reduced and money creating will be reduced. Policy 2: The government will use the other policy will use expansionary monetary policy for the small firms which can buy loans is to reduce the discount rate due to which it will be possible from them to take more credit and invest it in their business. Policy 3: Interest rates on credit cards would be lowered on starting from 10% to 17% of the current rates. More such declines in credit card interest rates for smaller firms and impacted persons have been proposed by institutions
a) Which of the three policies below do you think would be most
effective?
Policy 1:
Increments drive a contractionary financial approach in the different base loan costs constrained by current national banks or different methods creating development in cash flexibly. The objective is to lessen swelling by restricting the measure of dynamic cash coursing in the economy. In this when the government reduce the rate of interest then the supply of money will be reduced in the economy and contraction
Policy 2:
The government will use the other policy will use expansionary monetary policy for the small firms which can buy loans is to reduce the discount rate due to which it will be possible from them to take more credit and invest it in their business.
Policy 3:
Interest rates on credit cards would be lowered on starting from 10% to 17% of the current rates. More such declines in credit card interest rates for smaller firms and impacted persons have been proposed by institutions
Policy 1:
Central bank adopts the tight or contractionary monetary policy
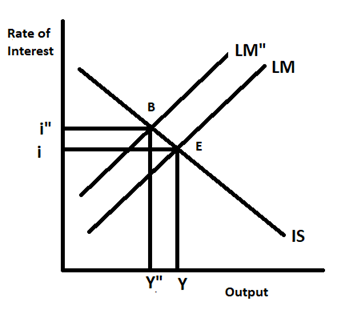
To control inflation the central banks adopt the contractionary monetary policy. In contractionary monetary policy, the central bank decreases the money supply in the economy through open market operations. It refers to the sale and purchase of government securities by the central bank in the open market. When the central bank sells the government securities in the open market the central banks receive currency funds and thus decrease the money supply.
As shown in the diagram when money supply decreases the LM curve shifts to the left from LM to LM". Due to this the leftward shift in the LM curve the interest rate rises from i to i" and output level falls from Y to Y". As the new equilibrium point moves from E to B.
Therefore the rise in interest rate will decrease the investment and consumption demand which helps in reducing inflation.
Policy 2:
The monetary policy basically leads to a change in the interest rate and money supply and all these changes are primarily done by the central bank. The main aim of the monetary policy is to target the inflation rate.
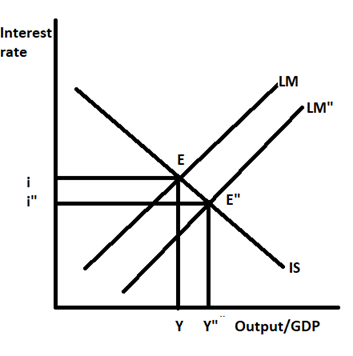
As shown in the diagram the downward sloping curve is the IS curve and the upward sloping is the LM curve. Both these curves intersect at point E, at the point of intersection the equilibrium interest rate is i and the equilibrium level of GDP is Y.
When a central bank increases the money supply in the economy then the LM curve shifts to the right and this rightward shift in the LM curve increases the GDP from Y to Y" and causes a decline in the interest rate from i to i".
In the case of recession the central bank adopts an expansionary monetary policy, this will increase the money supply and a higher money supply increases the lending of banks which causes a decrease in the interest rate and at lower interest rate loans becomes relatively cheaper and at a low-interest rate, the investment in the economy will rise. An increase in investment will increase aggregate demand. A rise in aggregate demand shifts the aggregate demand curve rightwards, as a result, the price level rises and output increases in the economy.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images


