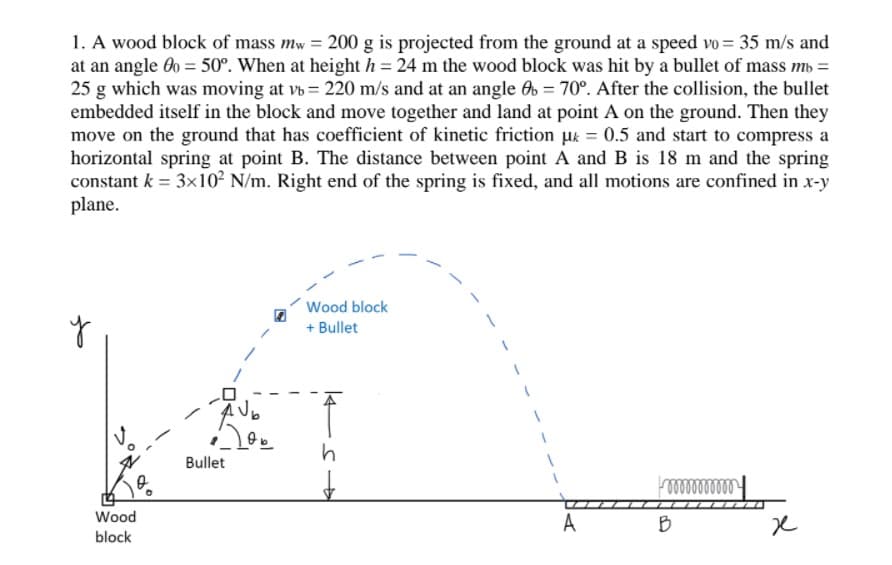
A woodblock of mass Mw = 200 g is projected from the ground at a speed v0 = 35 m/s and at an angle, θ0 = 50º. When at height h = 24 m the woodblock was hit by a bullet of mass Mb = 25 g which was moving at vb = 220 m/s and at an angle θb = 70º. After the collision, the bullet embedded itself in the block and move together and land at point A on the ground. Then they move on the ground that has a coefficient of kinetic friction µk = 0.5 and starts to compress a horizontal spring at point B. The distance between point A and B is 18 m and the spring constant k = 3×10^2 N/m. The right end of the spring is fixed, and all motions are confined in x-y plane. (a) Was the collision between the wood block and the bullet elastic or inelastic? Explain quantitively. (b) Find the maximum height from the ground the block with the bullet reached. (c) How far is point A from the launch point of the woodblock? (d) Calculate the velocity at which the block-bullet system lands at point A. What will be the speed of it at point B? (e) Determine how much the spring will be compressed when the block-bullet system comes to a rest.
A woodblock of mass Mw = 200 g is projected from the ground at a speed v0 = 35 m/s and at an angle, θ0 = 50º. When at height h = 24 m the woodblock was hit by a bullet of mass Mb = 25 g which was moving at vb = 220 m/s and at an angle θb = 70º. After the collision, the bullet embedded itself in the block and move together and land at point A on the ground. Then they move on the ground that has a coefficient of kinetic friction µk = 0.5 and starts to compress a horizontal spring at point B. The distance between point A and B is 18 m and the spring constant k = 3×10^2 N/m. The right end of the spring is fixed, and all motions are confined in x-y plane.
(a) Was the collision between the wood block and the bullet elastic or inelastic? Explain quantitively.
(b) Find the maximum height from the ground the block with the bullet reached.
(c) How far is point A from the launch point of the woodblock?
(d) Calculate the velocity at which the block-bullet system lands at point A. What will be the speed of it at point B?
(e) Determine how much the spring will be compressed when the block-bullet system comes to a rest.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps









