a. For this study, we should use Select an answer b. The null and alternative hypotheses would be: Ho✓ ? Select an arswer ✓ Select an answer ✓ Н1 Р P c. The test statistic ? = (please enter a decimal) (Please enter a decimal) (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.)
a. For this study, we should use Select an answer b. The null and alternative hypotheses would be: Ho✓ ? Select an arswer ✓ Select an answer ✓ Н1 Р P c. The test statistic ? = (please enter a decimal) (Please enter a decimal) (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.)
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
In question B where it has another drop down box the choices are:
=
>
<
Or unequal
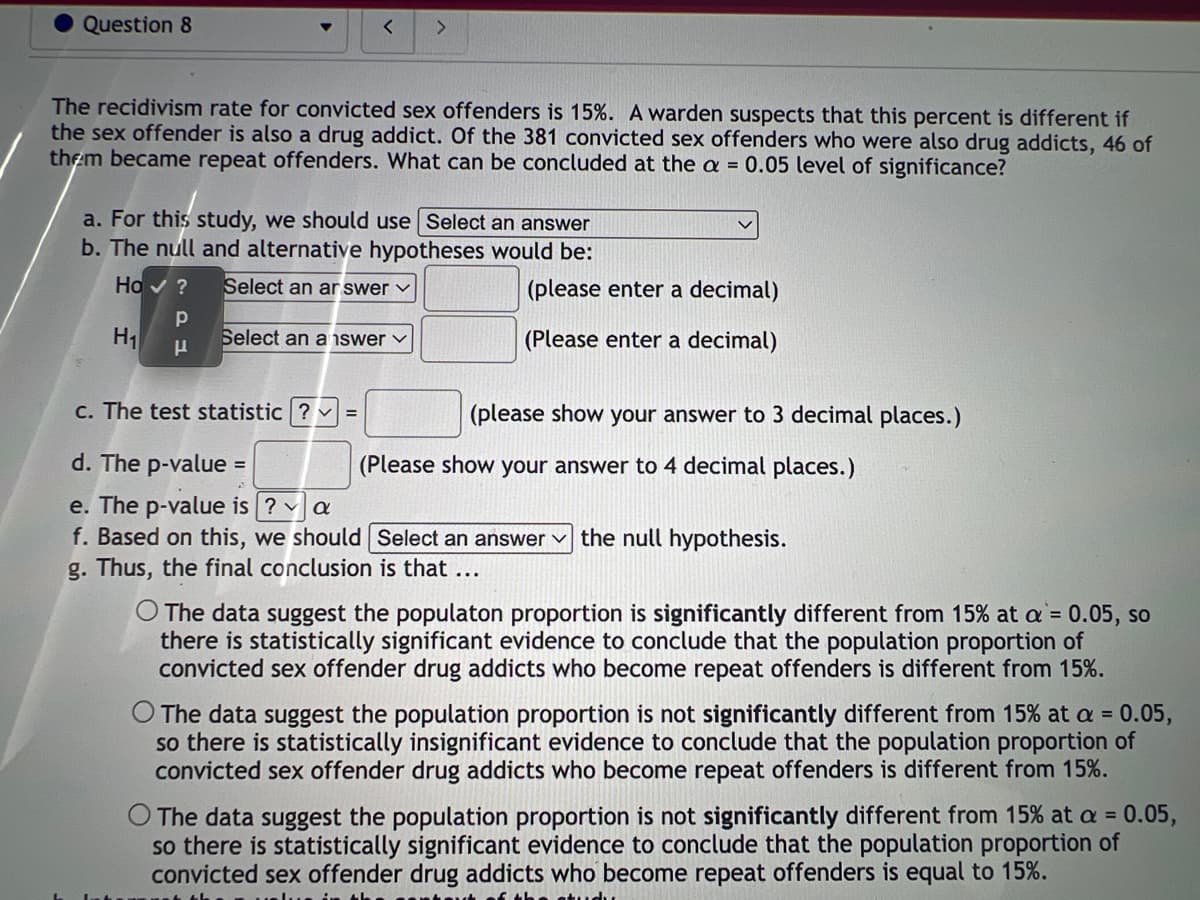
Transcribed Image Text:Question 8
The recidivism rate for convicted sex offenders is 15%. A warden suspects that this percent is different if
the sex offender is also a drug addict. Of the 381 convicted sex offenders who were also drug addicts, 46 of
them became repeat offenders. What can be concluded at the a = 0.05 level of significance?
< >
a. For this study, we should use Select an answer
b. The null and alternative hypotheses would be:
Ho✓ ?
Select an ar swer ✓
Р
P
Н1
Select an answer ✓
=
(please enter a decimal)
(Please enter a decimal)
c. The test statistic ? =
d. The p-value
e. The p-value is ? a
f. Based on this, we should Select an answer the null hypothesis.
g. Thus, the final conclusion is that ...
(please show your answer to 3 decimal places.)
(Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.)
O The data suggest the populaton proportion is significantly different from 15% at a = 0.05, so
there is statistically significant evidence to conclude that the population proportion of
convicted sex offender drug addicts who become repeat offenders is different from 15%.
O The data suggest the population proportion is not significantly different from 15% at a = 0.05,
so there is statistically insignificant evidence to conclude that the population proportion of
convicted sex offender drug addicts who become repeat offenders is different from 15%.
The data suggest the population proportion is not significantly different from 15% at a = 0.05,
so there is statistically significant evidence to conclude that the population proportion of
convicted sex offender drug addicts who become repeat offenders is equal to 15%.
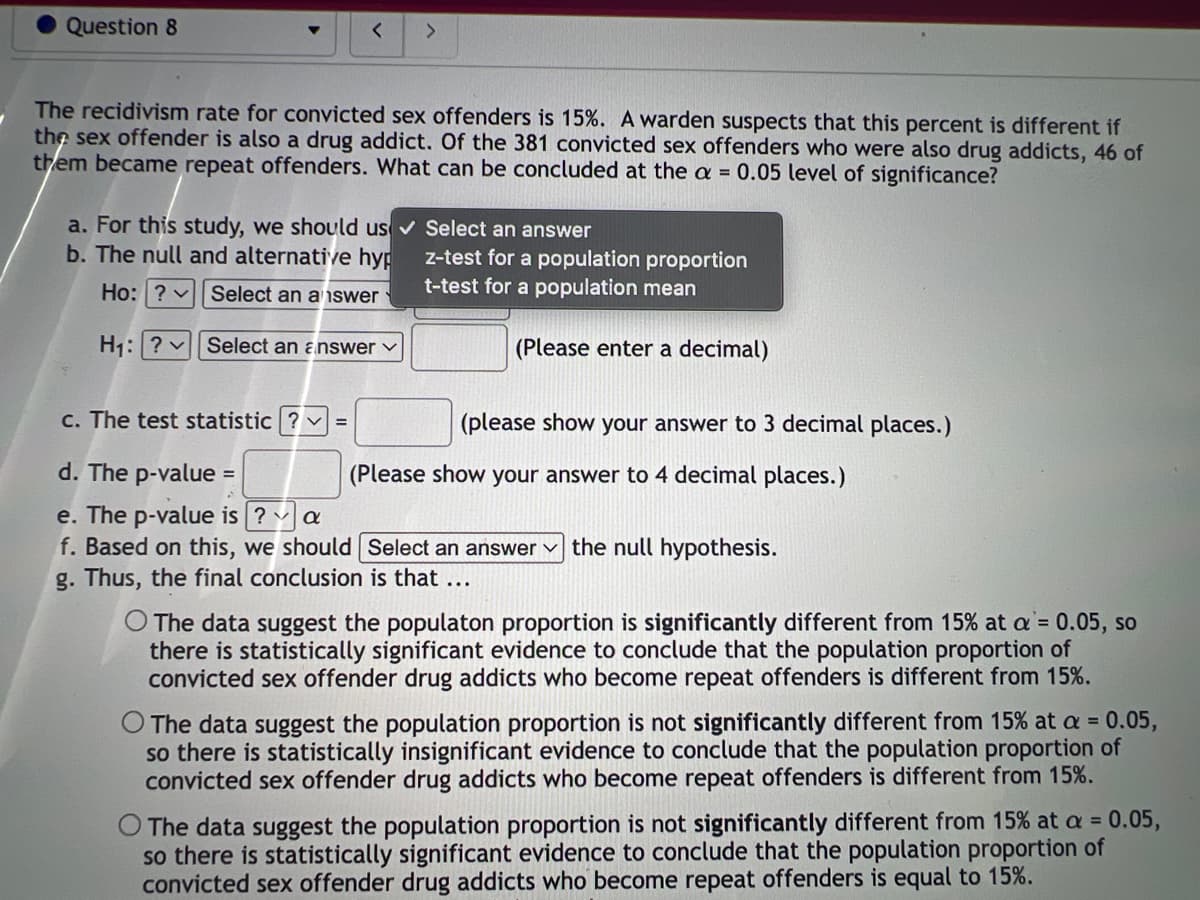
Transcribed Image Text:Question 8
<
>
The recidivism rate for convicted sex offenders is 15%. A warden suspects that this percent is different if
the sex offender is also a drug addict. Of the 381 convicted sex offenders who were also drug addicts, 46 of
them became repeat offenders. What can be concluded at the a = 0.05 level of significance?
a. For this study, we should us ✔ Select an answer
b. The null and alternative hyp
Select an answer
Ho: ?
H₁: ? Select an answer
z-test for a population proportion
t-test for a population mean
(Please enter a decimal)
c. The test statistic ? =
d. The p-value =
e. The p-value is ? a
f. Based on this, we should Select an answer the null hypothesis.
g. Thus, the final conclusion is that ...
(please show your answer to 3 decimal places.)
(Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.)
The data suggest the populaton proportion is significantly different from 15% at a = 0.05, so
there is statistically significant evidence to conclude that the population proportion of
convicted sex offender drug addicts who become repeat offenders is different from 15%.
O The data suggest the population proportion is not significantly different from 15% at a = 0.05,
so there is statistically insignificant evidence to conclude that the population proportion of
convicted sex offender drug addicts who become repeat offenders is different from 15%.
The data suggest the population proportion is not significantly different from 15% at a = 0.05,
so there is statistically significant evidence to conclude that the population proportion of
convicted sex offender drug addicts who become repeat offenders is equal to 15%.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman