A 9.30 L9.30 L container holds a mixture of two gases at 35 °C.35 °C. The partial pressures of gas A and gas B, respectively, are 0.296 atm0.296 atm and 0.504 atm.0.504 atm. If 0.180 mol0.180 mol of a third gas is added with no change in volume or temperature, what will the total pressure become?
A 9.30 L9.30 L container holds a mixture of two gases at 35 °C.35 °C. The partial pressures of gas A and gas B, respectively, are 0.296 atm0.296 atm and 0.504 atm.0.504 atm. If 0.180 mol0.180 mol of a third gas is added with no change in volume or temperature, what will the total pressure become?
Dalton's law:
Dalton's law of partial pressures states that in a mixture of non-reacting gases, the total pressure exerted is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases. The pressure of a mixture of non-reactive gases is given by:
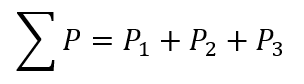
The partial pressure of gas A = 0.296 atm
The partial pressure of gas B = 0.504 atm
The partial pressure of gas C =?
Let calculate the partial pressure of the third gas:
For the ideal gas, the temperature pressure and the volume are related by the ideal gas equation. The ideal gas equation is given by:
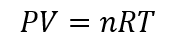
Here, P =pressure of the gas = ?
V = volume of the gas = 9.30 L
n = number of moles of the gas =0.180 mol
R = gas constant = 0.08205 L.atm.K-1mol-1
T = absolute temperature = 35oC = 35+273.15 = 308.15 K
By rearranging the above equation, we get:
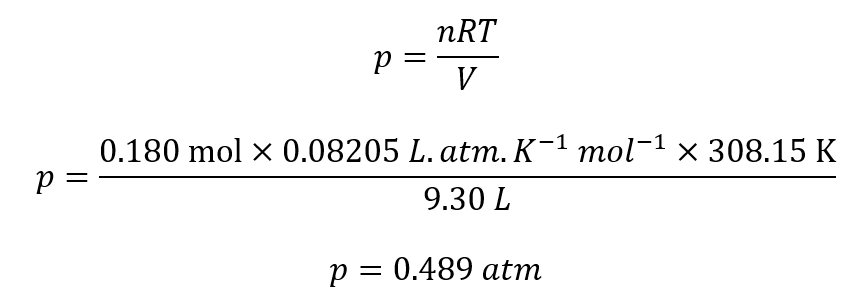
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images









