According to a study conducted five years ago by the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), the average length of stay in a hospital was 4.9 days in the United States. A researcher in the United States suspects that the average length of stay in a hospital has actually increased in the United States since the study was released by the OECD five years ago. To test his suspicion, the researcher selected a random sample of 191 hospital patients in the United States and calculated the average length of hospital stay. The mean of the sample was found to be 5.06 days. Using a = 0.005, test the hypothesis that the mean length of stay in a hospital in the United States is more than 4.9 days. Assume that the standard deviation of the lengths of all hospital stays in the United States is known to be 0.72 days. Use the p-value method. State the null and alternative hypothesis for this test.
According to a study conducted five years ago by the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), the average length of stay in a hospital was 4.9 days in the United States. A researcher in the United States suspects that the average length of stay in a hospital has actually increased in the United States since the study was released by the OECD five years ago. To test his suspicion, the researcher selected a random sample of 191 hospital patients in the United States and calculated the average length of hospital stay. The mean of the sample was found to be 5.06 days. Using a = 0.005, test the hypothesis that the mean length of stay in a hospital in the United States is more than 4.9 days. Assume that the standard deviation of the lengths of all hospital stays in the United States is known to be 0.72 days. Use the p-value method. State the null and alternative hypothesis for this test.
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8CR
Related questions
Question
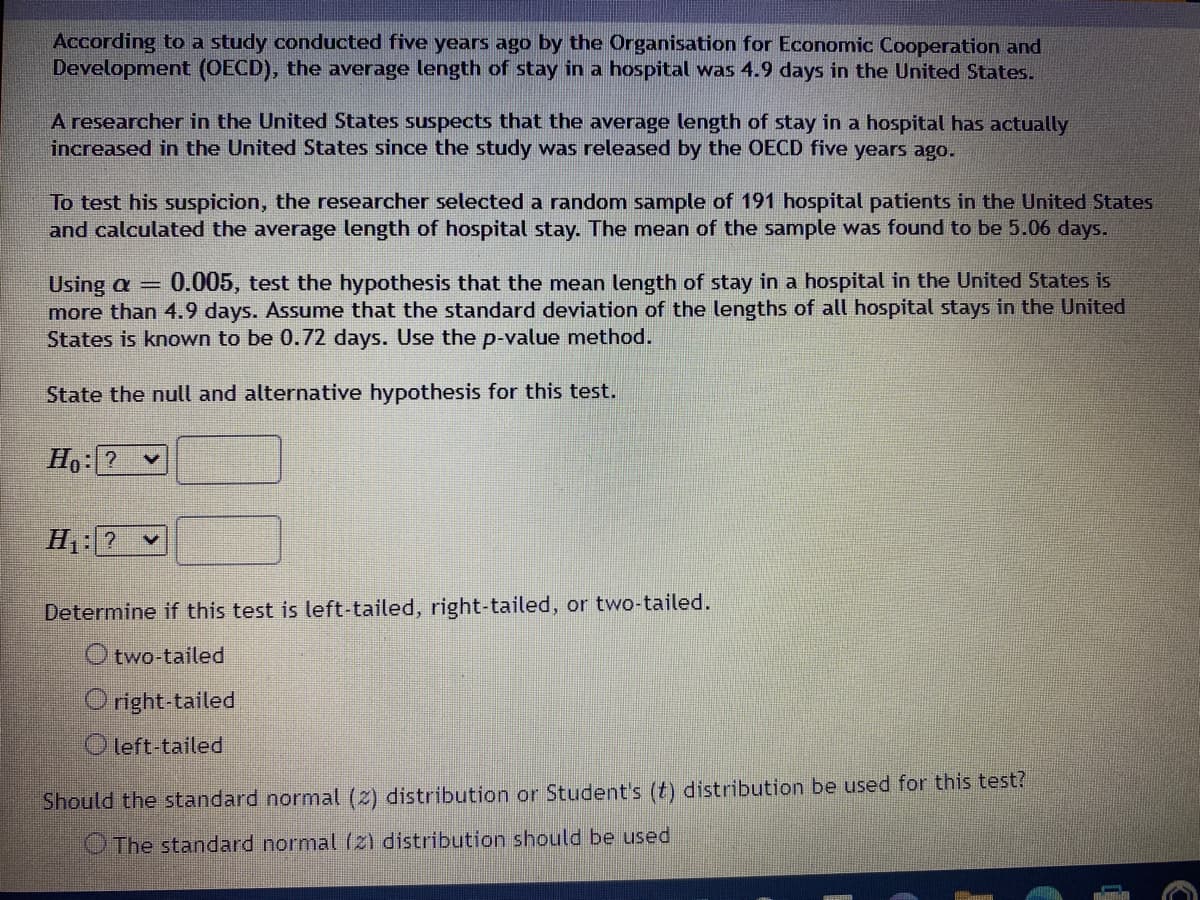
Transcribed Image Text:According to a study conducted five years ago by the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and
Development (OECD), the average length of stay in a hospital was 4.9 days in the United States.
A researcher in the United States suspects that the average length of stay in a hospital has actually
increased in the United States since the study was released by the OECD five years ago.
To test his suspicion, the researcher selected a random sample of 191 hospital patients in the United States
and calculated the average length of hospital stay. The mean of the sample was found to be 5.06 days.
Using a = 0.005, test the hypothesis that the mean length of stay in a hospital in the United States is
more than 4.9 days. Assume that the standard deviation of the lengths of all hospital stays in the United
States is known to be 0.72 days. Use the p-value method.
State the null and alternative hypothesis for this test.
Ho:?
H₁: ? ✓
Determine if this test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed.
two-tailed
right-tailed
Ⓒleft-tailed
Should the standard normal (2) distribution or Student's (t) distribution be used for this test?
The standard normal (2) distribution should be used
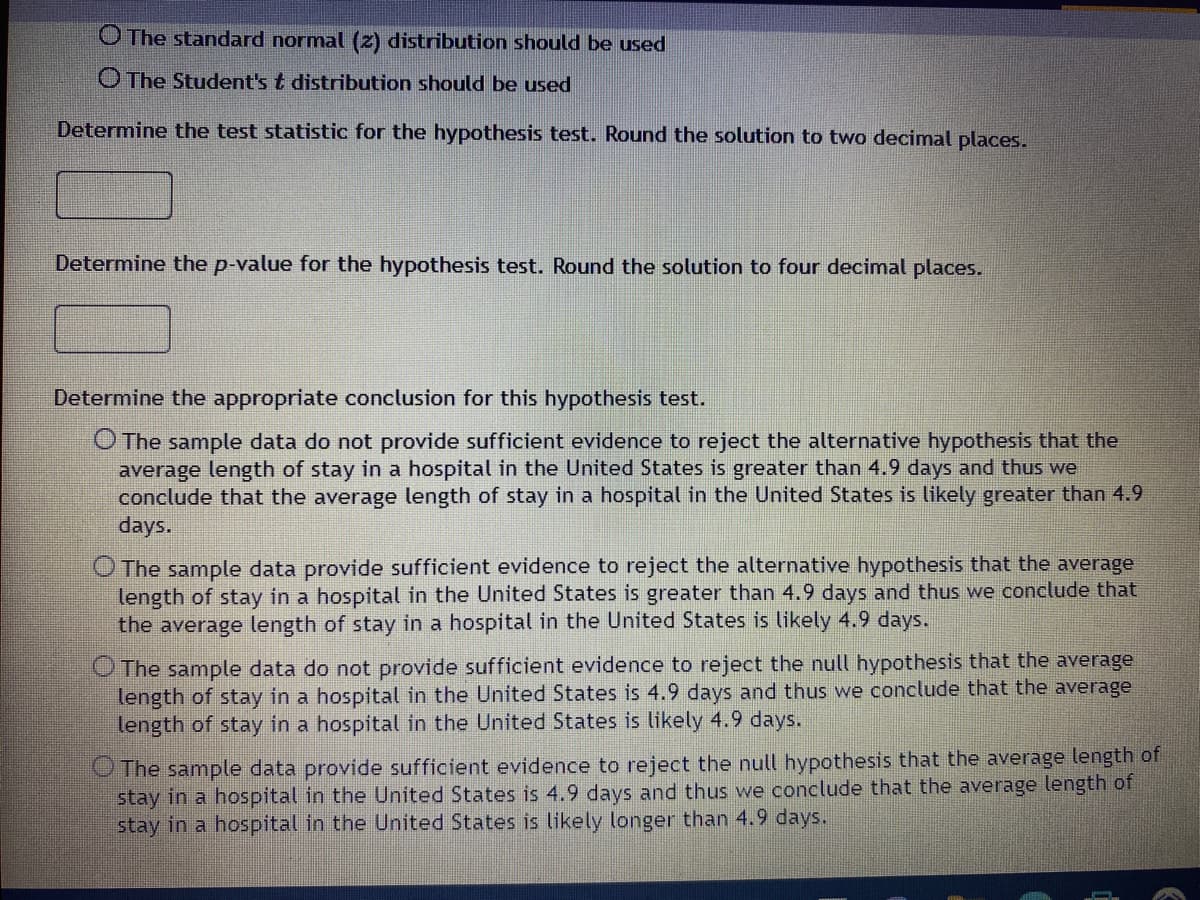
Transcribed Image Text:O The standard normal (z) distribution should be used
The Student's & distribution should be used
Determine the test statistic for the hypothesis test. Round the solution to two decimal places.
Determine the p-value for the hypothesis test. Round the solution to four decimal places.
Determine the appropriate conclusion for this hypothesis test.
O The sample data do not provide sufficient evidence to reject the alternative hypothesis that the
average length of stay in a hospital in the United States is greater than 4.9 days and thus we
conclude that the average length of stay in a hospital in the United States is likely greater than 4.9
days.
O The sample data provide sufficient evidence to reject the alternative hypothesis that the average
length of stay in a hospital in the United States is greater than 4.9 days and thus we conclude that
the average length of stay in a hospital in the United States is likely 4.9 days.
O The sample data do not provide sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis that the average
length of stay in a hospital in the United States is 4.9 days and thus we conclude that the average
length of stay in a hospital in the United States is likely 4.9 days.
O The sample data provide sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis that the average length of
stay in a hospital in the United States is 4.9 days and thus we conclude that the average length of
stay in a hospital in the United States is likely longer than 4.9 days.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL