Angular Momentum
The momentum of an object is given by multiplying its mass and velocity. Momentum is a property of any object that moves with mass. The only difference between angular momentum and linear momentum is that angular momentum deals with moving or spinning objects. A moving particle's linear momentum can be thought of as a measure of its linear motion. The force is proportional to the rate of change of linear momentum. Angular momentum is always directly proportional to mass. In rotational motion, the concept of angular momentum is often used. Since it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant—it is a significant quantity in physics. To understand the concept of angular momentum first we need to understand a rigid body and its movement, a position vector that is used to specify the position of particles in space. A rigid body possesses motion it may be linear or rotational. Rotational motion plays important role in angular momentum.
Moment of a Force
The idea of moments is an important concept in physics. It arises from the fact that distance often plays an important part in the interaction of, or in determining the impact of forces on bodies. Moments are often described by their order [first, second, or higher order] based on the power to which the distance has to be raised to understand the phenomenon. Of particular note are the second-order moment of mass (Moment of Inertia) and moments of force.
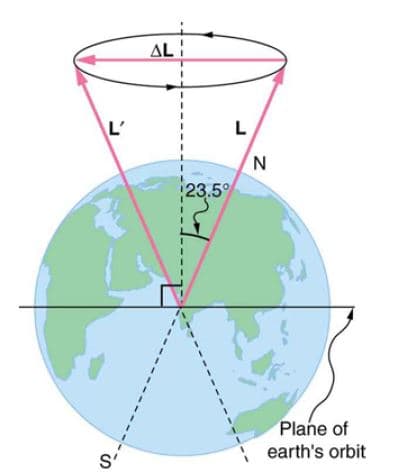
The axis of Earth makes a 23.5° angle with a direction perpendicular to the plane of Earth’s orbit. As shown, this axis precesses, making one complete
rotation in 25,780 y.
Calculate the change in
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









