Aluminum reacts with chlorine gas to form aluminum chloride via the following reaction: 2Al(s) + 3C12 (g)→2AICI3 (s) You are given 34.0 g of aluminum and 39.0 g of chlorine gas. Part A If you had excess chlorine, how many moles of of aluminum chloride could be produced from 34.0 g of aluminum? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. > View Available Hint(s) HA ? Value Units Part B If you had excess aluminum, how many moles of aluminum chloride could be produced from 39.0 g of chlorine gas, Cl2 ? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Aluminum reacts with chlorine gas to form aluminum chloride via the following reaction: 2Al(s) + 3C12 (g)→2AICI3 (s) You are given 34.0 g of aluminum and 39.0 g of chlorine gas. Part A If you had excess chlorine, how many moles of of aluminum chloride could be produced from 34.0 g of aluminum? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. > View Available Hint(s) HA ? Value Units Part B If you had excess aluminum, how many moles of aluminum chloride could be produced from 39.0 g of chlorine gas, Cl2 ? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter4: Stoichiometry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4.69PAE: 4.69 The pictures below show a molecular-scale view of a chemical reaction between H2 and CO to...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Aluminum reacts with chlorine gas to form
aluminum chloride via the following reaction:
2Al(s) + 3Cl2 (g)–→2AICI3 (s)
In the following chemical reaction, 2 mol of A will
react with 1 mol of B to produce 1 mol of A2 B
without anything left over:
You are given 34.0 g of aluminum and 39.0 g of
chlorine gas.
2A + B -A,В
But what if you're given 2.8 mol of A and 3.2 mol
of B? The amount of product formed is limited by
the reactant that runs out first, called the limiting
reactant. To identify the limiting reactant, calculate
the amount of product formed from each amount of
reactant separately:
Part A
If you had excess chlorine, how many moles of
of aluminum chloride could be produced from
34.0 g of aluminum?
1 mol A2B
2.8 metA x
= 1.4 mol A,B
2 mełA
Express your answer to three significant
figures and include the appropriate units.
1 mol A2B
3.2 motB x
3.2 mol A2B
• View Available Hint(s)
1 metB
Notice that less product is formed with the given
amount of reactant A. Thus, A is the limiting
reactant, and a maximum of 1.4 mol of A2B can
be formed from the given amounts.
HA
Value
Units
Part B
If you had excess aluminum, how many moles
of aluminum chloride could be produced from
39.0 g of chlorine gas, Cl2 ?
Express your answer to three significant
figures and include the appropriate units.
Expert Solution
Step 1
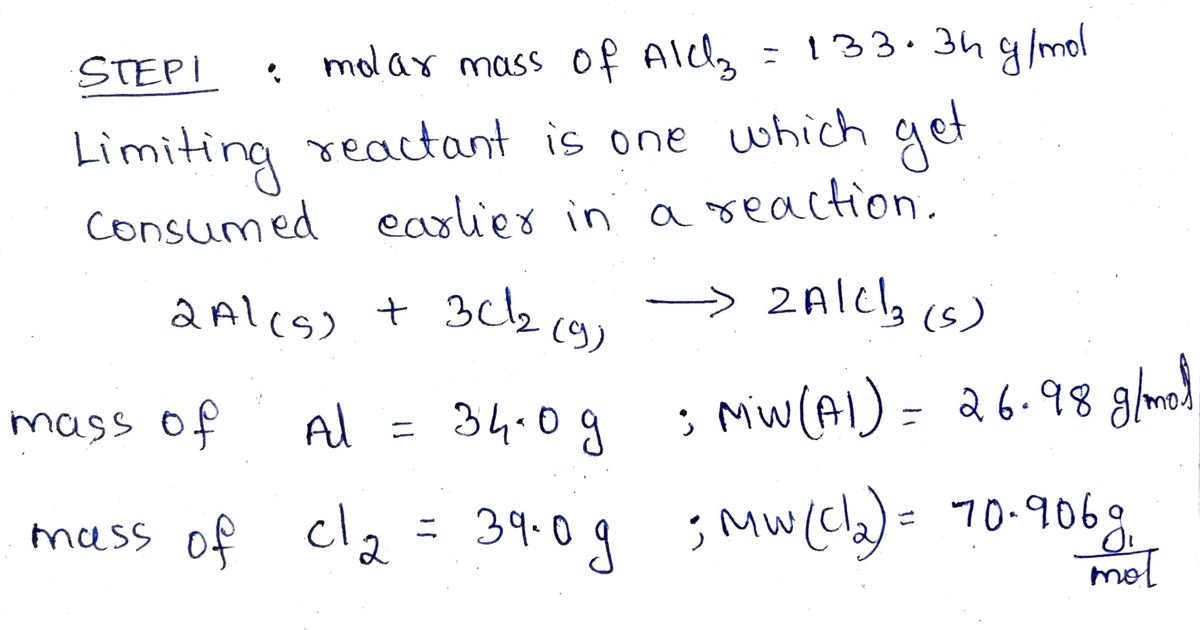
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
