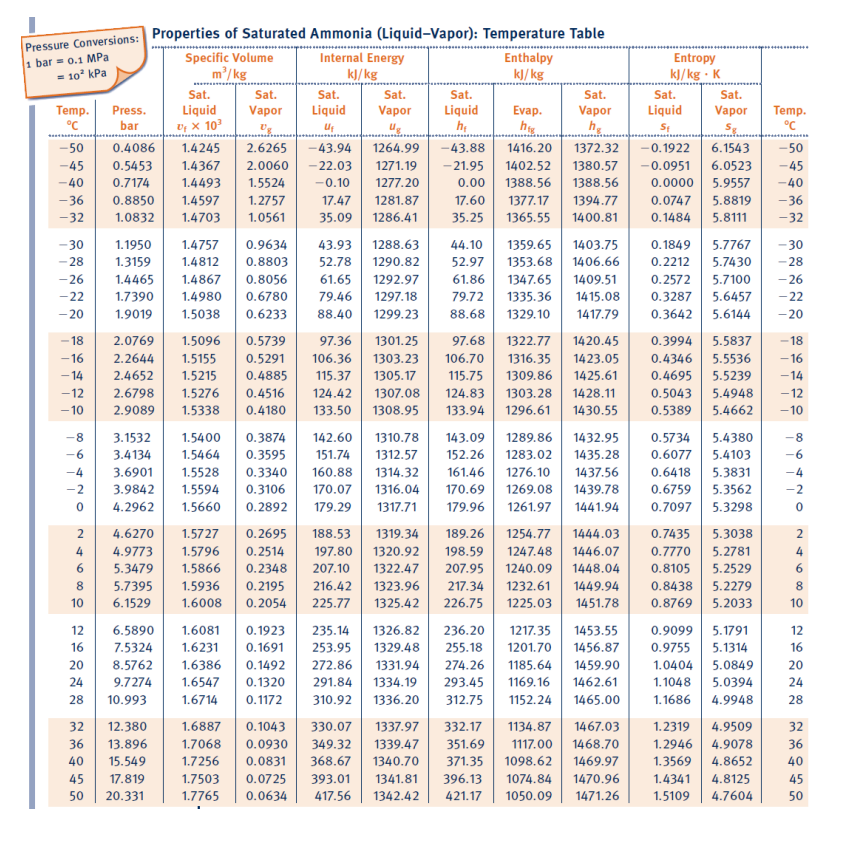
Ammonia in a piston-cylinder assembly undergoes two processes in series. Initially, the ammonia is saturated vapour at P₁=1000 kPa. Process 1-2 involves cooling until the piston meets the stops where the position is locked in place at which time quality is x2=75%. The second process from state 2 to state 3, involves heating (at constant volume) until x3=100%. If the mass is 0.45 kg determine: a) The work for process 1-2 (in kJ). b) The heat transfer for process 1-2 (in kJ). c) The work for process 2-3 (in kJ).
Ammonia in a piston-cylinder assembly undergoes two processes in series. Initially, the ammonia is saturated vapour at P₁=1000 kPa. Process 1-2 involves cooling until the piston meets the stops where the position is locked in place at which time quality is x2=75%. The second process from state 2 to state 3, involves heating (at constant volume) until x3=100%. If the mass is 0.45 kg determine: a) The work for process 1-2 (in kJ). b) The heat transfer for process 1-2 (in kJ). c) The work for process 2-3 (in kJ).
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Pressure Conversions: Properties of Saturated Ammonia (Liquid-Vapor): Temperature Table
1 bar = 0.1 MPa
Specific Volume
Internal Energy
= 10² kPa
m³/kg
kJ/kg
Temp.
°C
-30 1.1950 1.4757
-28 1.3159 1.4812
-26
-22
-20
-8
-6
-50
0.4086
-43.94
1.4245 2.6265
1.4367 2.0060 -22.03
-45 0.5453
-40 0.7174
1.4493
1.5524
-0.10
-36 0.8850 1.4597 1.2757
17.47
35.09
-32 1.0832
1.4703 1.0561
-4
-2
0
2
4
6
Press.
bar
8
10
1.4465
1.7390
1.9019
20
24
28
Sat.
Liquid
Uf X 10²
-18
2.0769
-16
1.5096 0.5739 97.36 1301.25
2.2644 1.5155 0.5291 106.36 1303.23
-14 2.4652 1.5215 0.4885 115.37 1305.17
-12 2.6798 1.5276 0.4516 124.42 1307.08
-10 2.9089 1.5338 0.4180 133.50 1308.95
4.6270
4.9773
5.3479
0.9634
0.8803
1.4867
0.8056
1.4980 0.6780
1.5038
0.6233
3.1532 1.5400
3.4134 1.5464
3.6901 1.5528
3.9842 1.5594
4.2962
1.5660
Sat.
Vapor
Ug
32 12.380
36 13.896
40 15.549
17.819
45
50 20.331
1.5727
1.5796
1.5866
6.5890 1.6081
12
16 7.5324 1.6231
8.5762 1.6386
9.7274 1.6547
10.993
1.6714
Sat.
Liquid
UF
5.7395 1.5936 0.2195
6.1529
1.6008 0.2054
0.2514
0.2348
0.3874
142.60
1310.78
151.74 1312.57
0.3595
0.3340
0.3106 170.07
160.88 1314.32
1316.04
0.2892 179.29 1317.71
43.93 1288.63
52.78 1290.82
61.65 1292.97
79.46 1297.18
88.40 1299.23
0.2695 188.53
0.1923
0.1691
0.1492
0.1320
0.1172
Sat.
Sat.
Sat.
Vapor
Liquid
Liquid
Ug
h₁
Sf
1264.99 -43.88 1416.20 1372.32 -0.1922
1271.19 -21.95 1402.52 1380.57 -0.0951
1277.20
0.00 1388.56 1388.56 0.0000
1281.87 17.60 1377.17 1394.77
1286.41 35.25 1365.55 1400.81
1319.34
197.80 1320.92
1322.47
207.10
216.42
1323.96
225.77
1325.42
Enthalpy
kJ/kg
143.09
152.26
161.46
170.69
179.96
Evap.
hig
44.10 1359.65 1403.75
52.97 1353.68 1406.66
61.86 1347.65 1409.51
79.72 1335.36 1415.08
88.68 1329.10 1417.79
235.14
1326.82
253.95 1329.48
272.86 1331.94
291.84 1334.19
1336.20 312.75
310.92
Sat.
Vapor
hg
97.68 1322.77 1420.45
106.70 1316.35 1423.05
115.75 1309.86 1425.61
124.83 1303.28 1428.11
133.94 1296.61 1430.55
1289.86 1432.95
1283.02 1435.28
1276.10 1437.56
1269.08 1439.78
1261.97 1441.94
189.26 1254.77 1444.03
198.59 1247.48 1446.07
207.95 1240.09 1448.04
217.34 1232.61 1449.94
226.75 1225.03 1451.78
1217.35 1453.55
236.20
255.18 1201.70
274.26 1185.64 1459.90
293.45 1169.16 1462.61
1152.24 1465.00
Entropy
kJ/kg. K
1.6887
0.1043 330.07
1134.87 1467.03
1337.97 332.17
1.7068 0.0930 349.32 1339.47 351.69 1117.00 1468.70
1.7256 0.0831 368.67 1340.70 371.35 1098.62 1469.97
393.01 1341.81 396.13 1074.84 1470.96
417.56 1342.42 421.17 1050.09 1471.26
1.7503
0.0725
1.7765
0.0634
Sat.
Vapor
5g
6.0523
5.9557
0.0747 5.8819
0.1484
5.8111
0.2572
0.3287
0.3642
6.1543 -50
0.1849 5.7767
0.2212 5.7430
5.7100
5.6457
5.6144
0.5734 5.4380
0.6077 5.4103
0.6418 5.3831
0.6759 5.3562
0.7097 5.3298
0.9099 5.1791
1456.87 0.9755 5.1314
1.0404 5.0849
1.1048 5.0394
1.1686 4.9948
0.7435 5.3038
0.7770 5.2781
0.8105 5.2529
0.8438 5.2279
0.8769 5.2033
0.3994 5.5837
0.4346 5.5536
0.4695 5.5239 -14
0.5043 5.4948 -12
0.5389 5.4662 -10
Temp.
°℃
1.2319 4.9509
1.2946 4.9078
1.3569 4.8652
1.4341 4.8125
1.5109 4.7604
-45
-40
-36
-32
-30
-28
-26
-22
-20
-18
-16
-8
-6
-4
-2
0
2
4
6
8
10
26048
12
16
28
32
36
40
45
50

Transcribed Image Text:Ammonia in a piston-cylinder assembly undergoes two processes in series. Initially, the ammonia
is saturated vapour at P₁=1000 kPa. Process 1-2 involves cooling until the piston meets the stops
where the position is locked in place at which time quality is x2=75%. The second process from
state 2 to state 3, involves heating (at constant volume) until x3=100%. If the mass is 0.45 kg
determine:
a) The work for process 1-2 (in kJ).
b) The heat transfer for process 1-2 (in kJ).
c) The work for process 2-3 (in kJ).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY