An artificial lung receives venous blood from a patient at a rate of 5 litres per minute. The venous blood has partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) of 40 mmH and partial pressure of carb dioxide (PCO2) of 45 mg. Given the dissociation curves for oxygen and carbon dioxide shown in Figure Q3a: Calculate the gas exchange rates required from the artificial lung to ensure the blood returned to the patient has PO2 of 100 mmH and PCO2 of 40 mmH. Show your calculations. O₂ concentration (ml per 100 ml) 22 18 14 10- 6 2 0 20 40 60 PO₂ (mmHg) 80 100 CO₂ concentration (ml per 100 ml) 60- 50 40 30- 20- 10. 0 20 40 60 PCO, (mmHg) Figure Q3a Dissociation curves for oxygen and carbon dioxide in blood 80
An artificial lung receives venous blood from a patient at a rate of 5 litres per minute. The venous blood has partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) of 40 mmH and partial pressure of carb dioxide (PCO2) of 45 mg. Given the dissociation curves for oxygen and carbon dioxide shown in Figure Q3a: Calculate the gas exchange rates required from the artificial lung to ensure the blood returned to the patient has PO2 of 100 mmH and PCO2 of 40 mmH. Show your calculations. O₂ concentration (ml per 100 ml) 22 18 14 10- 6 2 0 20 40 60 PO₂ (mmHg) 80 100 CO₂ concentration (ml per 100 ml) 60- 50 40 30- 20- 10. 0 20 40 60 PCO, (mmHg) Figure Q3a Dissociation curves for oxygen and carbon dioxide in blood 80
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Lauralee Sherwood
Chapter13: The Respiratory System
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1SQE
Related questions
Question
Please atleast answer this question. I will upvote
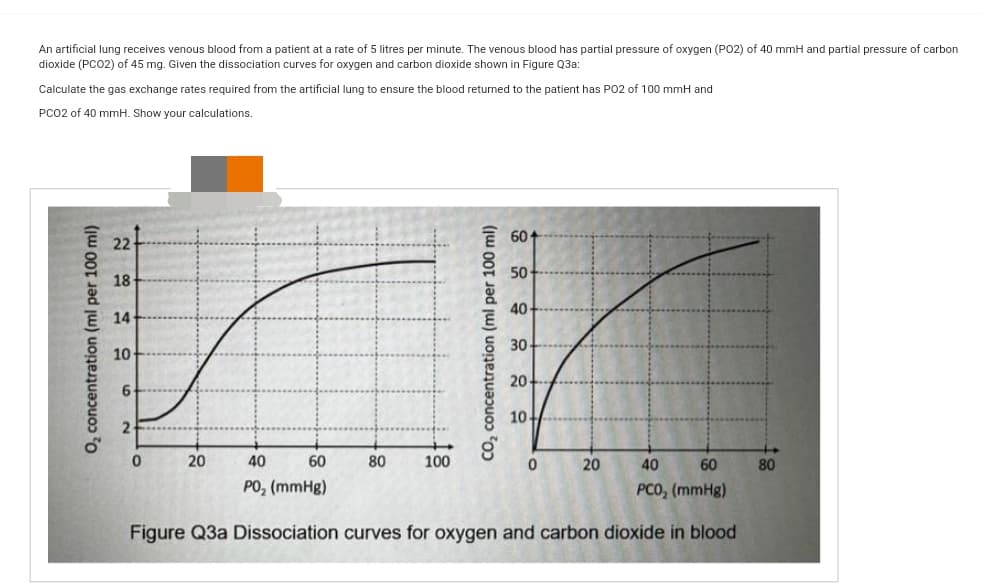
Transcribed Image Text:An artificial lung receives venous blood from a patient at a rate of 5 litres per minute. The venous blood has partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) of 40 mmH and partial pressure of carbon
dioxide (PCO2) of 45 mg. Given the dissociation curves for oxygen and carbon dioxide shown in Figure Q3a:
Calculate the gas exchange rates required from the artificial lung to ensure the blood returned to the patient has PO2 of 100 mmH and
PCO2 of 40 mmH. Show your calculations.
O₂ concentration (ml per 100 ml)
22
18
14
10
6
2
0
20
40
60
PO₂ (mmHg)
80
100
CO₂ concentration (ml per 100 ml)
60
40
30
20
10+
40
60
PCO, (mmHg)
Figure Q3a Dissociation curves for oxygen and carbon dioxide in blood
0
20
80
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Basic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C…
Nursing
ISBN:
9781285244662
Author:
White
Publisher:
Cengage

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Basic Clinical Lab Competencies for Respiratory C…
Nursing
ISBN:
9781285244662
Author:
White
Publisher:
Cengage

Cardiopulmonary Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781337794909
Author:
Des Jardins, Terry.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305112100
Author:
Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning