An ideal vapor-compression refrigeration cycle that uses refrigerant-134a as its working fluid maintains a condenser at 800 kPa and the temperature of the evaporator is -15 C. Given 300 kW of cooling load, determine the following: 4. Determine the Refrigeration effect (RE), heat of compression (HOC), and heat of rejection (HOR) and their corresponding rate/power values in kW. 5. Estimate the COPR using thermodynamic tables 6. Calculate the COPR using the P-h chart and show the refrigeration cycle on the p-h chart. 7. Discuss the difference between your answers in 4 and 5 above and which one do you think is more accurate.
An ideal vapor-compression refrigeration cycle that uses refrigerant-134a as its working fluid maintains a condenser at 800 kPa and the temperature of the evaporator is -15 C. Given 300 kW of cooling load, determine the following: 4. Determine the Refrigeration effect (RE), heat of compression (HOC), and heat of rejection (HOR) and their corresponding rate/power values in kW. 5. Estimate the COPR using thermodynamic tables 6. Calculate the COPR using the P-h chart and show the refrigeration cycle on the p-h chart. 7. Discuss the difference between your answers in 4 and 5 above and which one do you think is more accurate.
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305578296
Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Chapter47: High-pressure, Low-pressure, And Absorption Chilled-water Systems
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13RQ: The subcooling temperature in a condenser can be measured by taking the difference between the A....
Related questions
Question
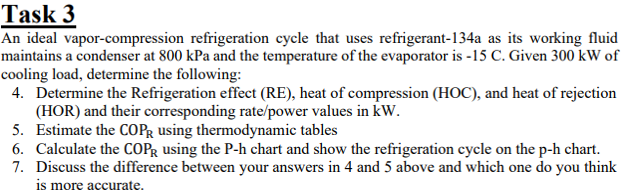
Transcribed Image Text:Task 3
An ideal vapor-compression refrigeration cycle that uses refrigerant-134a as its working fluid
maintains a condenser at 800 kPa and the temperature of the evaporator is -15 C. Given 300 kW of
cooling load, determine the following:
4. Determine the Refrigeration effect (RE), heat of compression (HOC), and heat of rejection
(HOR) and their corresponding rate/power values in kW.
5. Estimate the COPR using thermodynamic tables
6. Calculate the COPR using the P-h chart and show the refrigeration cycle on the p-h chart.
7. Discuss the difference between your answers in 4 and 5 above and which one do you think
is more accurate.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning