An important issue in conservation biology is how dispersal among populations influences the persistence of species in a fragmented landscape. Molofsky and Ferdy (2005) measured this in the annual plant, Cardamine pensylvanica, a weed that produces explosively dispersed seeds. Four treatments were used to manipulate seed dispersal by changing the distance among experimental plant populations. These treatments were adjacent (continuous treatment), separated by 23.2 cm (medium), separated by 49.5 cm (long), or separated by partitions that blocked all seed dispersal among populations (isolated). Treatments were randomly assigned to plant populations. The data shown are the number of generations that the populations persisted in six replicates of each treatment. Test whether the persistence of species differ with distance among experimental plant populations at 5% significance level. Conduct a follow up analysis when necessary. Treatment Generations persisted Isolated 9 8 8 8 8 9 Medium 14 9. 16 16 16 15 Long 13 9. 10 11 11 9 Continuous 9 13 13 16 13 13
An important issue in conservation biology is how dispersal among populations influences the persistence of species in a fragmented landscape. Molofsky and Ferdy (2005) measured this in the annual plant, Cardamine pensylvanica, a weed that produces explosively dispersed seeds. Four treatments were used to manipulate seed dispersal by changing the distance among experimental plant populations. These treatments were adjacent (continuous treatment), separated by 23.2 cm (medium), separated by 49.5 cm (long), or separated by partitions that blocked all seed dispersal among populations (isolated). Treatments were randomly assigned to plant populations. The data shown are the number of generations that the populations persisted in six replicates of each treatment. Test whether the persistence of species differ with distance among experimental plant populations at 5% significance level. Conduct a follow up analysis when necessary. Treatment Generations persisted Isolated 9 8 8 8 8 9 Medium 14 9. 16 16 16 15 Long 13 9. 10 11 11 9 Continuous 9 13 13 16 13 13
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter7: Distance And Approximation
Section7.3: Least Squares Approximation
Problem 31EQ
Related questions
Question
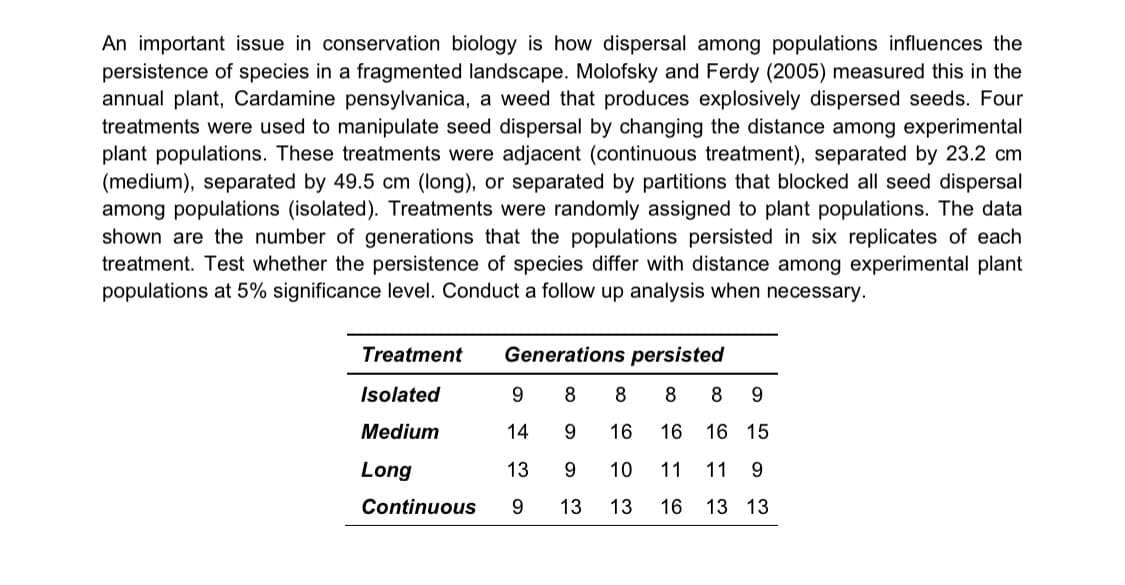
Transcribed Image Text:An important issue in conservation biology is how dispersal among populations influences the
persistence of species in a fragmented landscape. Molofsky and Ferdy (2005) measured this in the
annual plant, Cardamine pensylvanica, a weed that produces explosively dispersed seeds. Four
treatments were used to manipulate seed dispersal by changing the distance among experimental
plant populations. These treatments were adjacent (continuous treatment), separated by 23.2 cm
(medium), separated by 49.5 cm (long), or separated by partitions that blocked all seed dispersal
among populations (isolated). Treatments were randomly assigned to plant populations. The data
shown are the number of generations that the populations persisted in six replicates of each
treatment. Test whether the persistence of species differ with distance among experimental plant
populations at 5% significance level. Conduct a follow up analysis when necessary.
Treatment
Generations persisted
Isolated
9
8
8
8
8
Medium
14
16
16
16 15
Long
13
9.
10
11
11
9
Continuous
9
13
13
16
13 13
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning