An important measure in the study of contagious infectious diseases is the number of cases directly generated by one previous case. Ashley is an epidemiologist studying the spread of an infectious disease in her country. She claimed that the mean number of cases directly generated by one previous case is now greater than 2.6. A study of 18 randomly selected cases of the disease is conducted and finds the sample mean number of cases directly generated by one previous case to be 3.1 with a sample standard deviation of 1.1. Assume that the population of the number of cases directly generated by one previous case is approximately normally distributed. Complete the parts below to perform a hypothesis test to see if there is enough evidence, at the 0.05 level of significance, to support the claim that H, the mean number of cases directly generated by one previous case, is greater than 2.6. (a) State the null hypothesis H, and the alternative hypothesis H, that you would use for the test. H: p= 2.6 H: p> 2.6 ロ<ロ ロSロ ロ=ロ ロロ Student's t Distribution Step 1: Enter the number of degrees of freedom. 0.4+ Step 2: Select one-tailed or two-tailed. O One-tailed 0.3 O Two-tailed Step 3: Enter the test statistic. (Round to 3 decimal places.) 1.928 0.2- Step 4: Shade the area represented by the p-value. 0.1 Step 5: Enter the p-value. (Round to 3 decimal places.) 0.035
An important measure in the study of contagious infectious diseases is the number of cases directly generated by one previous case. Ashley is an epidemiologist studying the spread of an infectious disease in her country. She claimed that the mean number of cases directly generated by one previous case is now greater than 2.6. A study of 18 randomly selected cases of the disease is conducted and finds the sample mean number of cases directly generated by one previous case to be 3.1 with a sample standard deviation of 1.1. Assume that the population of the number of cases directly generated by one previous case is approximately normally distributed. Complete the parts below to perform a hypothesis test to see if there is enough evidence, at the 0.05 level of significance, to support the claim that H, the mean number of cases directly generated by one previous case, is greater than 2.6. (a) State the null hypothesis H, and the alternative hypothesis H, that you would use for the test. H: p= 2.6 H: p> 2.6 ロ<ロ ロSロ ロ=ロ ロロ Student's t Distribution Step 1: Enter the number of degrees of freedom. 0.4+ Step 2: Select one-tailed or two-tailed. O One-tailed 0.3 O Two-tailed Step 3: Enter the test statistic. (Round to 3 decimal places.) 1.928 0.2- Step 4: Shade the area represented by the p-value. 0.1 Step 5: Enter the p-value. (Round to 3 decimal places.) 0.035
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897, 0079039898, 2018
18th Edition
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:Carter
Chapter10: Statistics
Section10.3: Measures Of Spread
Problem 1GP
Related questions
Question
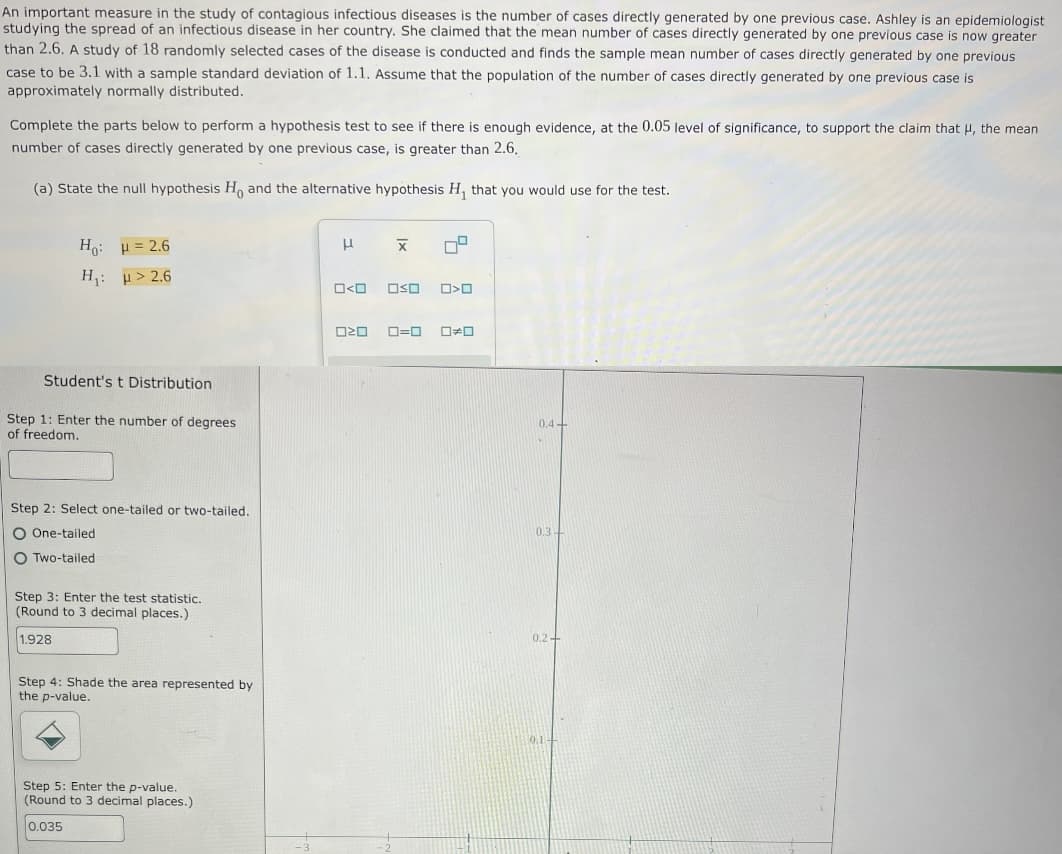
Transcribed Image Text:An important measure in the study of contagious infectious diseases is the number of cases directly generated by one previous case. Ashley is an epidemiologist
studying the spread of an infectious disease in her country. She claimed that the mean number of cases directly generated by one previous case is now greater
than 2.6. A study of 18 randomly selected cases of the disease is conducted and finds the sample mean number of cases directly generated by one previous
case to be 3.1 with a sample standard deviation of 1.1. Assume that the population of the number of cases directly generated by one previous case is
approximately normally distributed.
Complete the parts below to perform a hypothesis test to see if there is enough evidence, at the 0.05 level of significance, to support the claim that H, the mean
number of cases directly generated by one previous case, is greater than 2.6.
(a) State the null hypothesis H, and the alternative hypothesis H, that you would use for the test.
H: p = 2.6
Η: μ>2.6
ロ<ロ
ロSロ
ロ>ロ
ロ=ロ
ロロ
Student's t Distribution
Step 1: Enter the number of degrees
of freedom.
0.4+
Step 2: Select one-tailed or two-tailed.
O One-tailed
0.3
O Two-tailed
Step 3: Enter the test statistic.
(Round to 3 decimal places.)
1.928
0.2-
Step 4: Shade the area represented by
the p-value.
0.1
Step 5: Enter the p-value.
(Round to 3 decimal places.)
0.035

Transcribed Image Text:(c) Based on your answer to part (b), choose what can be concluded, at the 0.05 level of significance, about the claim made by Ashley.
O Since the p-value is less than (or equal to) the level of significance, the null hypothesis is rejected. So, there is
enough evidence to support the claim that the mean number of cases directly generated by one previous case is
greater than 2.6.
Since the p-value is less than (or equal to) the level of significance, the null hypothesis is not rejected. So, there is
not enough evidence to support the claim that the mean number of cases directly generated by one previous case is
greater than 2.6.
Since the p-value is greater than the level of significance, the null hypothesis is rejected. So, there is enough
evidence to support the claim that the mean number of cases directly generated by one previous case is greater than
2.6.
O Since the p-value is greater than the level of significance, the null hypothesis is not rejected. So, there is not enough
evidence to support the claim that the mean number of cases directly generated by one previous case is greater than
2.6.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill