Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Chapter10: Properties Of Solutions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7RQ
Related questions
Question
Analyze the figure below and describe what happens to the colligative properties when solute is added to the solution.
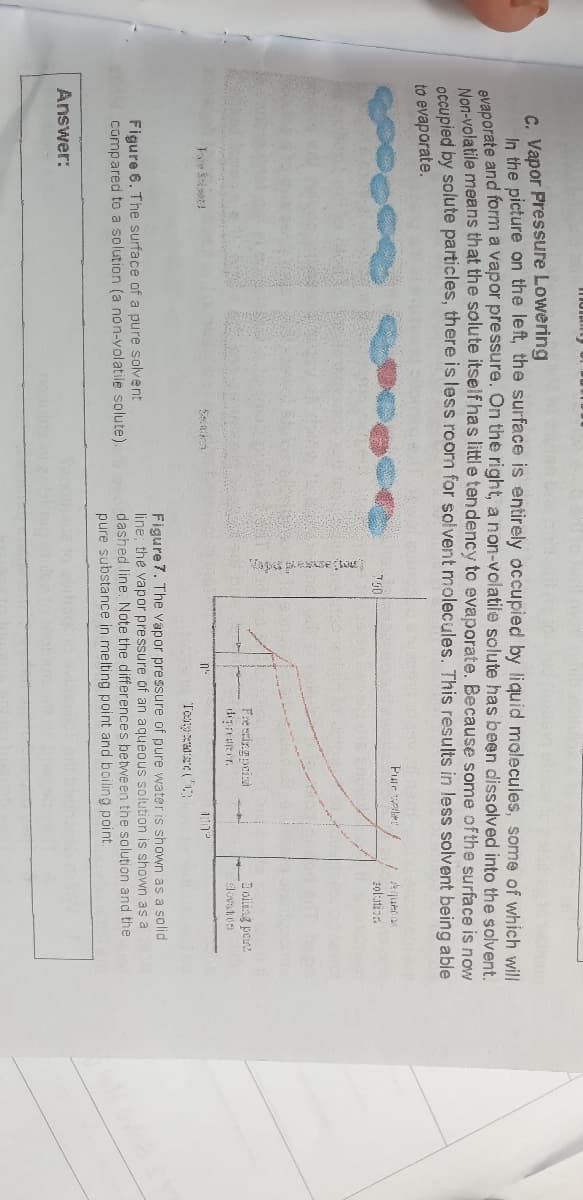
Transcribed Image Text:C. Vapor Pressure Lowering
In the picture on the left, the surface is entirely occupied by liquid molecules, some of which will
avaporate and form a vapor pressure. On the right, a non-volatile solute has been dissolved into the solvent.
Nan-volatile means that the solute itself has little tendency to evaporate. Because some of the surface is now
OCGupied by solute particles, there is less room for solvent molecules. This results in less solvent being able
to evaporate.
Pule weler
zolutior.
Fre eing pois
I oiting peue
n'-
1:1
Teaya(
Figure 6. The surface of a pure solvent
compared to a solution (a non-volatile solute).
Figure 7. The vapor pressure of pure water is shown as a solid
line: the vapor pressure of an agyeous solution is shown as a
dashed line. Note the differences between the solution and the
pure substance in melting point and boiling point.
Answer:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780534420123
Author:
Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079113
Author:
David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC L
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305446021
Author:
Lampman
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT