Antibiotic A: 0.5 kDa protein, targets peptidoglycan Antibiotic B: 20 kDa protein, targets peptidoglycan Antibiotic C: Cationic antimicrobial peptide Antibiotic D: Targets lipopolysaccharide Staphylococcus aureus: gram-positive bacterium Vibrio cholera: gram-negative
Antibiotic A: 0.5 kDa protein, targets peptidoglycan Antibiotic B: 20 kDa protein, targets peptidoglycan Antibiotic C: Cationic antimicrobial peptide Antibiotic D: Targets lipopolysaccharide Staphylococcus aureus: gram-positive bacterium Vibrio cholera: gram-negative
Basic Clinical Laboratory Techniques 6E
6th Edition
ISBN:9781133893943
Author:ESTRIDGE
Publisher:ESTRIDGE
Chapter7: Basic Clinical Microbiology
Section7.7: Bacterial Identification And Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
Problem 4RQ
Related questions
Question
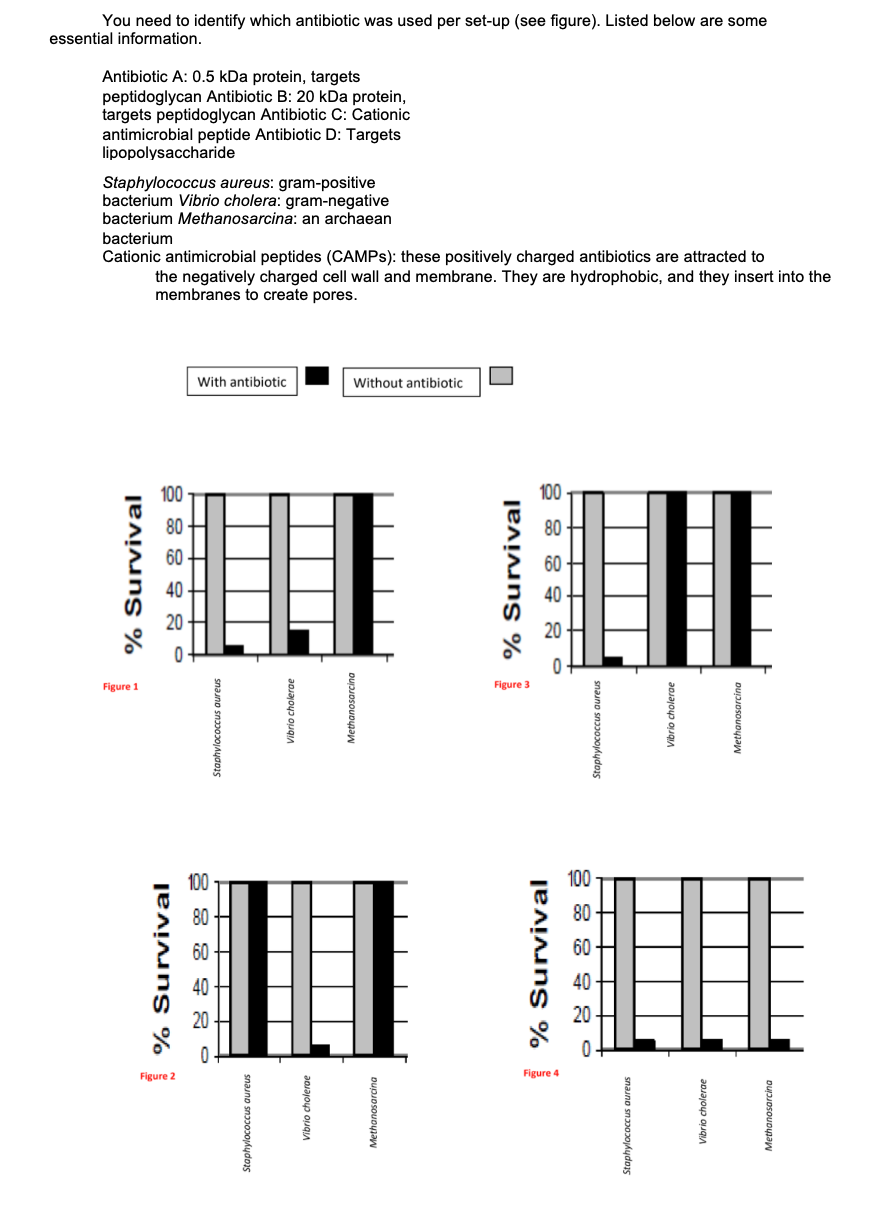
Transcribed Image Text:You need to identify which antibiotic was used per set-up (see figure). Listed below are some
essential information.
Antibiotic A: 0.5 kDa protein, targets
peptidoglycan Antibiotic B: 20 kDa protein,
targets peptidoglycan Antibiotic C: Cationic
antimicrobial peptide Antibiotic D: Targets
lipopolysaccharide
Staphylococcus aureus: gram-positive
bacterium Vibrio cholera: gram-negative
bacterium Methanosarcina: an archaean
bacterium
Cationic antimicrobial peptides (CAMPS): these positively charged antibiotics are attracted to
the negatively charged cell wall and membrane. They are hydrophobic, and they insert into the
membranes to create pores.
With antibiotic
Without antibiotic
100
100
80-
80
60
60
40
40
20
Figure 1
Figure 3
100
100
80
80
60
60
40
20
20
Figure 2
Figure 4
% Survival
| % Survival
aphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus
E
Vibrio cholerae
Vibrio cholerae
lethanosarcina
Methanosarcina
! % Survival
| % Survival
-- ▬▬-
Staphylococcus aureus
snajno sna300jdydos
Vibrio cholerae
Vibrio cholerae
Methanosarcing
Methanosarcina
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you



